Spring核心容器体系结构
1.BeanFactory
SpringBean的创建是典型的工厂模式,这一系列的Bean工厂,也即IOC容器为开发者管理对象间的依赖关系提供了很多便利和基础服务,在Spring中有许多的IOC容器的实现供用户选择和使用.
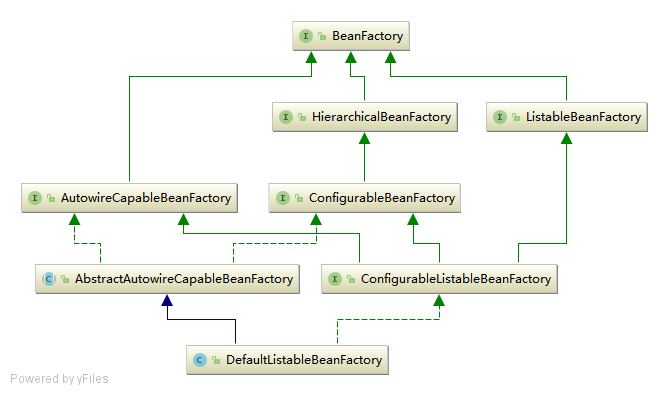
BeanFactory作为最顶层的一个接口类,它定义了IOC容器的基本功能规范BeanFactory有三个子类, 主要是为了区分在Spring内部在操作过程中对象的传递和转化过程中,对对象的数据访问所做的限制:ListableBeanFactory: 表示这些Bean是可列表的HierarchicalBeanFactory: 表示的是这些Bean是有继承关系的,也就是每个Bean有可能有父BeanAutowireCapableBeanFactory: 定义Bean的自动装配规则
BeanFactory最终的默认实现类是DefaultListableBeanFactory,他实现了所有的接口
这四个接口共同定义了Bean的集合、Bean之间的关系、以及Bean行为
1.1 最基本的IOC容器接口BeanFactory
public interface BeanFactory {
/**
* 对于FactoryBean的转义定义,因为如果使用bean的名字检索FactoryBean得到的对象是工厂生成的对象
* 如果需要得到工厂本身,需要转义
*/
String FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX = "&";
/**
* 根据bean的名字,获取在IOC容器中得到bean实例
*/
Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException;
/**
* 根据bean的名字和Class类型来得到bean实例,增加了类型安全验证机制
*/
<T> T getBean(String name, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException;
Object getBean(String name, Object... args) throws BeansException;
<T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException;
<T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType, Object... args) throws BeansException;
/**
* 提供对bean的检索,看看是否在IOC容器有这个名字的bean
*/
boolean containsBean(String name);
/**
* 根据bean名字得到bean实例,并同时判断这个bean是不是单例
*/
boolean isSingleton(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
boolean isPrototype(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
boolean isTypeMatch(String name, ResolvableType typeToMatch) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
boolean isTypeMatch(String name, @Nullable Class<?> typeToMatch) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
/**
* 得到bean实例的Class类型
*/
@Nullable
Class<?> getType(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
/**
* 得到bean的别名,如果根据命名检索,那么其原名也会被检索出来
*/
String[] getAliases(String name);
}
在BeanFactory里只对IOC容器的基本行为作了定义,根本不关心你的Bean是如何定义怎样加载的.正如我们只关心工厂里得到什么的产品对象,至于工厂是怎么生产这些对象的,这个基本的接口不关心.
1.2 DefaultListableBeanFactory
XmlBeanFactory继承自DefaultListableBeanFactory,而DefaultListableBeanFactory是整个bean加载的核心部分,是Spring注册及加载bean的默认实现,而对于XmlBeanFactory与DefaultListableBeanFactory不同的地方其实是在XmlBeanFactory中使用了自定义的XML读取器XmlBeanDefinitionReader,实现了个性化的BeanDefinitionReader读取,DefaultListableBeanFactory继承了AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory并实现了ConfigURableListableBeanFactory以及BeanDefinitionRegistry接口.
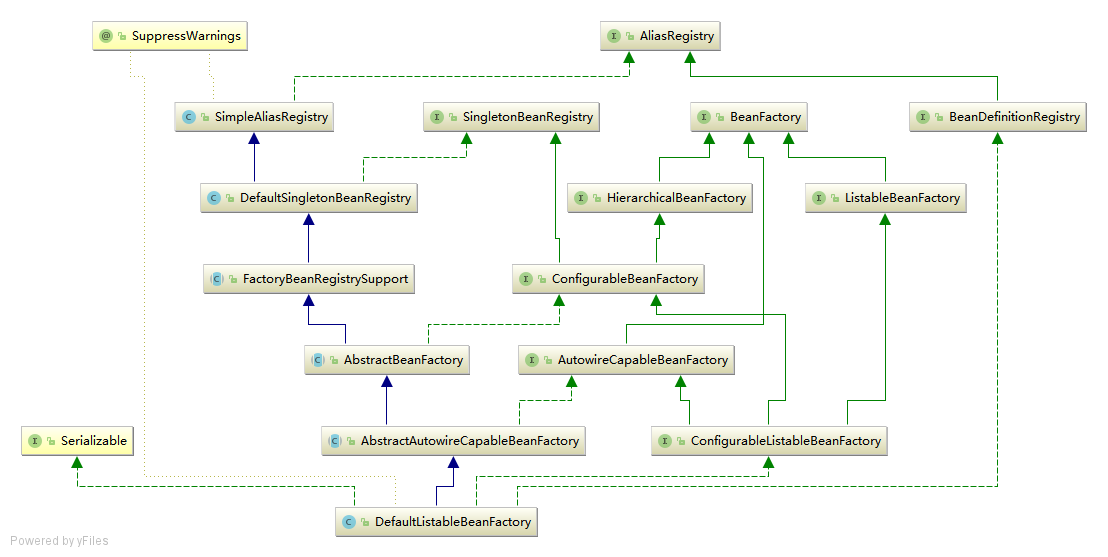
类图中各个类的作用:
AliasRegistry: 定义对alias的简单增删改等操作SimpleAliasRegistry: 主要使用map作为alias的缓存,并对接口AliasRegistry进行实现SingletonBeanRegistry: 定义对单例的注册及获取BeanFactory: 定义获取bean及bean的各种属性DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry: 对接口SingletonBeanRegistry各函数的实现HierarchicalBeanFactory: 继承BeanFactory,也就是在BeanFactory定义的功能的基础上增加了对parentFactory的支持BeanDefinitionRegistry: 定义对BeanDefinition的各种增删改操作FactoryBeanRegistrySupport: 在DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry基础上增加了对FactoryBean的特殊处理功能ConfigurableBeanFactory: 提供配置Factory的各种方法ListableBeanFactory: 根据各种条件获取bean的配置清单AbstractBeanFactory: 综合FactoryBeanRegistrySupport和ConfigurationBeanFactory的功能AutowireCapableBeanFactory: 提供创建bean、自动注入、初始化以及应用bean的后处理器AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory: 综合AbstractBeanFactory并对接口AutowireCapableBeanFactory进行实现ConfigurableListableBeanFactory:BeanFactory配置清单,指定忽略类型及接口等DefaultListableBeanFactory: 综合上面所有功能,主要是对Bean注册后的处理
2.ApplicationContext
要知道工厂是如何产生对象的,我们需要看具体的IOC容器实现,Spring提供了许多IOC容器的实现.比如XmlBeanFactory,ClasspathXmlApplicationContext等.其中XmlBeanFactory就是针对最基本的IOC容器的实现,这个IOC容器可以读取XML文件定义的BeanDefinition(XML文件中对bean的描述),如果说XmlBeanFactory是容器中的屌丝,ApplicationContext应该算容器中的高帅富.
ApplicationContext是Spring提供的一个高级的IOC容器,它除了能够提供IOC容器的基本功能外,还为用户提供了以下的附加服务.
public interface ApplicationContext extends EnvironmentCapable, ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory,
MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher, ResourcePatternResolver {
/**
* Return the unique id of this application context.
* @return the unique id of the context, or {@code null} if none
*/
@Nullable
String getId();
/**
* Return a name for the deployed application that this context belongs to.
* @return a name for the deployed application, or the empty String by default
*/
String getApplicationName();
/**
* Return a friendly name for this context.
* @return a display name for this context (never {@code null})
*/
String getDisplayName();
/**
* Return the timestamp when this context was first loaded.
* @return the timestamp (ms) when this context was first loaded
*/
long getStartupDate();
/**
* Return the parent context, or {@code null} if there is no parent
* and this is the root of the context hierarchy.
* @return the parent context, or {@code null} if there is no parent
*/
@Nullable
ApplicationContext getParent();
/**
* Expose AutowireCapableBeanFactory functionality for this context.
* <p>This is not typically used by application code, except for the purpose of
* initializing bean instances that live outside of the application context,
* applying the Spring bean lifecycle (fully or partly) to them.
* <p>Alternatively, the internal BeanFactory exposed by the
* {@link ConfigurableApplicationContext} interface offers access to the
* {@link AutowireCapableBeanFactory} interface too. The present method mainly
* serves as a convenient, specific facility on the ApplicationContext interface.
* <p><b>NOTE: As of 4.2, this method will consistently throw IllegalStateException
* after the application context has been closed.</b> In current Spring Framework
* versions, only refreshable application contexts behave that way; as of 4.2,
* all application context implementations will be required to comply.
* @return the AutowireCapableBeanFactory for this context
* @throws IllegalStateException if the context does not support the
* {@link AutowireCapableBeanFactory} interface, or does not hold an
* autowire-capable bean factory yet (e.g. if {@code refresh()} has
* never been called), or if the context has been closed already
* @see ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh()
* @see ConfigurableApplicationContext#getBeanFactory()
*/
AutowireCapableBeanFactory getAutowireCapableBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException;
}
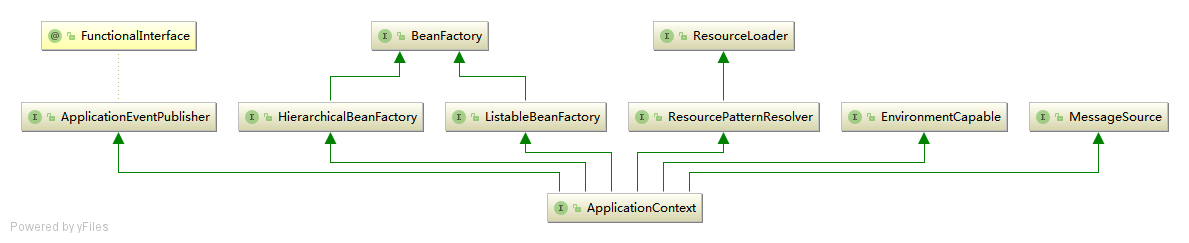
从ApplicationContext接口的实现,我们看出其特点:
- 支持信息源,可以实现国际化.(实现
MessageSource接口) - 访问资源.(实现
ResourcePatternResolver接口,后面章节会讲到) - 支持应用事件.(实现
ApplicationEventPublisher接口)
3.BeanDefinition
SpringIOC容器管理了我们定义的各种Bean对象及其相互的关系,Bean对象在Spring实现中是以BeanDefinition来描述的,其继承体系如下:
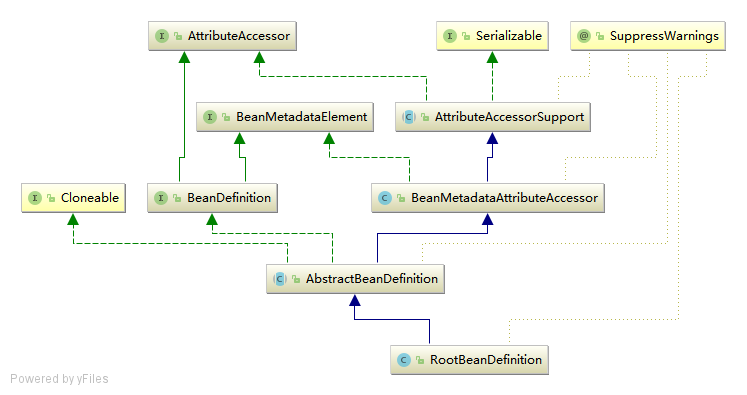
Bean的解析过程非常复杂,功能被分的很细,因为这里需要被扩展的地方很多,必须保证有足够的灵活性,以应对可能的变化.Bean的解析主要就是对Spring配置文件的解析.
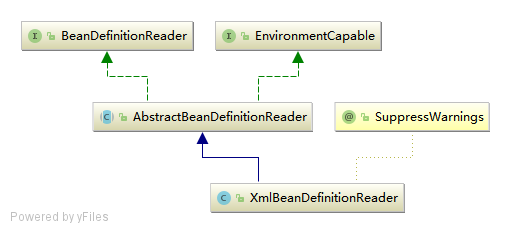
4.Resource
Spring的配置文件读取是通过ClassPathResource进行封装的,Spring对其内部使用到的资源实现了自己的抽象结构: Resource接口来封装底层资源.
public interface InputStreamSource {
InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException;
}
/**
* Spring 框架所有资源的抽象和访问接口
*/
public interface Resource extends InputStreamSource {
/**
* 资源是否存在
*/
boolean exists();
/**
* 资源是否可读
*/
default boolean isReadable() {
return exists();
}
/**
* 资源所代表的句柄是否被一个 stream 打开了
*/
default boolean isOpen() {
return false;
}
/**
* 是否为 File
*/
default boolean isFile() {
return false;
}
/**
* 返回资源的 URL 的句柄
*/
URL getURL() throws IOException;
/**
* 返回资源的 URI 的句柄
*/
URI getURI() throws IOException;
/**
* 返回资源的 File 的句柄
*/
File getFile() throws IOException;
/**
* 返回 ReadableByteChannel
*/
default ReadableByteChannel readableChannel() throws IOException {
return Channels.newChannel(getInputStream());
}
/**
* 资源内容的长度
*/
long contentLength() throws IOException;
/**
* 资源最后的修改时间
*/
long lastModified() throws IOException;
/**
* 根据资源的相对路径创建新资源
*/
Resource createRelative(String relativePath) throws IOException;
/**
* 资源的文件名
*/
@Nullable
String getFilename();
/**
* 资源的描述
*/
String getDescription();
}
Resource接口抽象了所有Spring内部使用到的底层资源:File、URL、Classpath等.
- 定义了3个判断当前资源状态的方法: 存在性(exists)、可读性(isReadable)、是否处于打开状态(isOpen).
- 还提供了不同资源到URL、URI、File类型的转换,以及获取lastModified属性、文件名(不带路径信息的文件名,
getFilename())的方法 - 提供了基于当前资源创建一个相对资源的方法:
createRelative() - 提供了
getDescription()方法用于在错误处理中的打印信息

当通过Resource相关类完成了对配置文件进行封装后,配置文件的读取工作就全权交给XmlBeanDefinitionReader来处理了.