ChannelPipeline和ChannelHandler
Netty的ChannelPipeline和ChannelHandler机制类似于Servlet和Filter过滤器,前者将Channel的数据管道抽象为ChannelPipeline,消息在该pipeline中流动和传递,内部维护了ChannelHandler的链表,由这些handler对IO事件进行拦截和处理
1.ChannelPipeline
ChannelPipeline是ChannelHandler的容器,它负责ChannelHandler的管理和事件拦截与调度
1.1 ChannelPipeline事件
1.1.1 事件处理流程
I/O Request
via {@link Channel} or
{@link ChannelHandlerContext}
|
+---------------------------------------------------+---------------+
| ChannelPipeline | |
| \|/ |
| +---------------------+ +-----------+----------+ |
| | Inbound Handler N | | Outbound Handler 1 | |
| +----------+----------+ +-----------+----------+ |
| /|\ | |
| | \|/ |
| +----------+----------+ +-----------+----------+ |
| | Inbound Handler N-1 | | Outbound Handler 2 | |
| +----------+----------+ +-----------+----------+ |
| /|\ . |
| . . |
| ChannelHandlerContext.fireIN_EVT() ChannelHandlerContext.OUT_EVT()|
| [ method call] [method call] |
| . . |
| . \|/ |
| +----------+----------+ +-----------+----------+ |
| | Inbound Handler 2 | | Outbound Handler M-1 | |
| +----------+----------+ +-----------+----------+ |
| /|\ | |
| | \|/ |
| +----------+----------+ +-----------+----------+ |
| | Inbound Handler 1 | | Outbound Handler M | |
| +----------+----------+ +-----------+----------+ |
| /|\ | |
+---------------+-----------------------------------+---------------+
| \|/
+---------------+-----------------------------------+---------------+
| | | |
| [ Socket.read() ] [ Socket.write() ] |
| |
| Netty Internal I/O Threads (Transport Implementation) |
+-------------------------------------------------------------------+
一个消息被ChannelPipeline的ChannelHandler链拦截和处理的全过程:
- 底层的
SocketChannel read()方法读取ByteBuf,触发ChannelRead事件,由I/O线程NioEventLoop调用ChannelPipeline的fireChannelRead(Object msg)方法,将消息(ByteBuf)传输到ChannelPipeline中 - 消息依次被
HeadHandler、ChannelHandler1、ChannelHandler2……TailHandler拦截和处理,在这个过程中,任何ChannelHandler都可以中断当前的流程,结束消息的传递 - 调用
ChannelHandlerContext的write方法发送消息,消息从TailHandler开始,途经ChannelHandlerN……ChannelHandler1、HeadHandler,最终被添加到消息发送缓冲区中等待刷新和发送,在此过程中也可以中断消息的传递,例如当编码失败时,就需要中断流程,构造异常的Future返回
1.1.2 事件分类
Netty中的事件分为inbound事件和outbound事件
- inbound事件通常由I/O线程触发,例如TCP链路建立事件、链路关闭事件、读事件、异常通知事件等
- 触发inbound事件的方法如下
ChannelHandlerContext.fireChannelRegistered(): Channel注册事件ChannelHandlerContext.fireChannelActive(): TCP链路建立成功,Channel激活事件ChannelHandlerContext.fireChannelRead(Object): 读事件ChannelHandlerContext.fireChannelReadComplete(): 读操作完成通知事件ChannelHandlerContext.fireExceptionCaught(Throwable): 异常通知事件ChannelHandlerContext.fireUserEventTriggered(Object): 用户自定义事件ChannelHandlerContext.fireChannelWritabilityChanged(): Channel的可写状态变化通知事件ChannelHandlerContext.fireChannelInactive(): TCP连接关闭,链路不可用通知事件
- 触发inbound事件的方法如下
- Outbound事件通常是由用户主动发起的网络I/O操作,例如用户发起的连接操作、绑定操作、消息发送等操作
- 触发outbound事件的方法如下:
ChannelHandlerContext.bind(SocketAddress, ChannelPromise): 绑定本地地址事件ChannelHandlerContext.connect(SocketAddress, SocketAddress, ChannelPromise): 连接服务端事件ChannelHandlerContext.write(Object, ChannelPromise): 发送事件ChannelHandlerContext.flush(): 刷新事件ChannelHandlerContext.read(): 读事件ChannelHandlerContext.disconnect(ChannelPromise): 断开连接事件ChannelHandlerContext.close(ChannelPromise): 关闭当前Channel事件
- 触发outbound事件的方法如下:
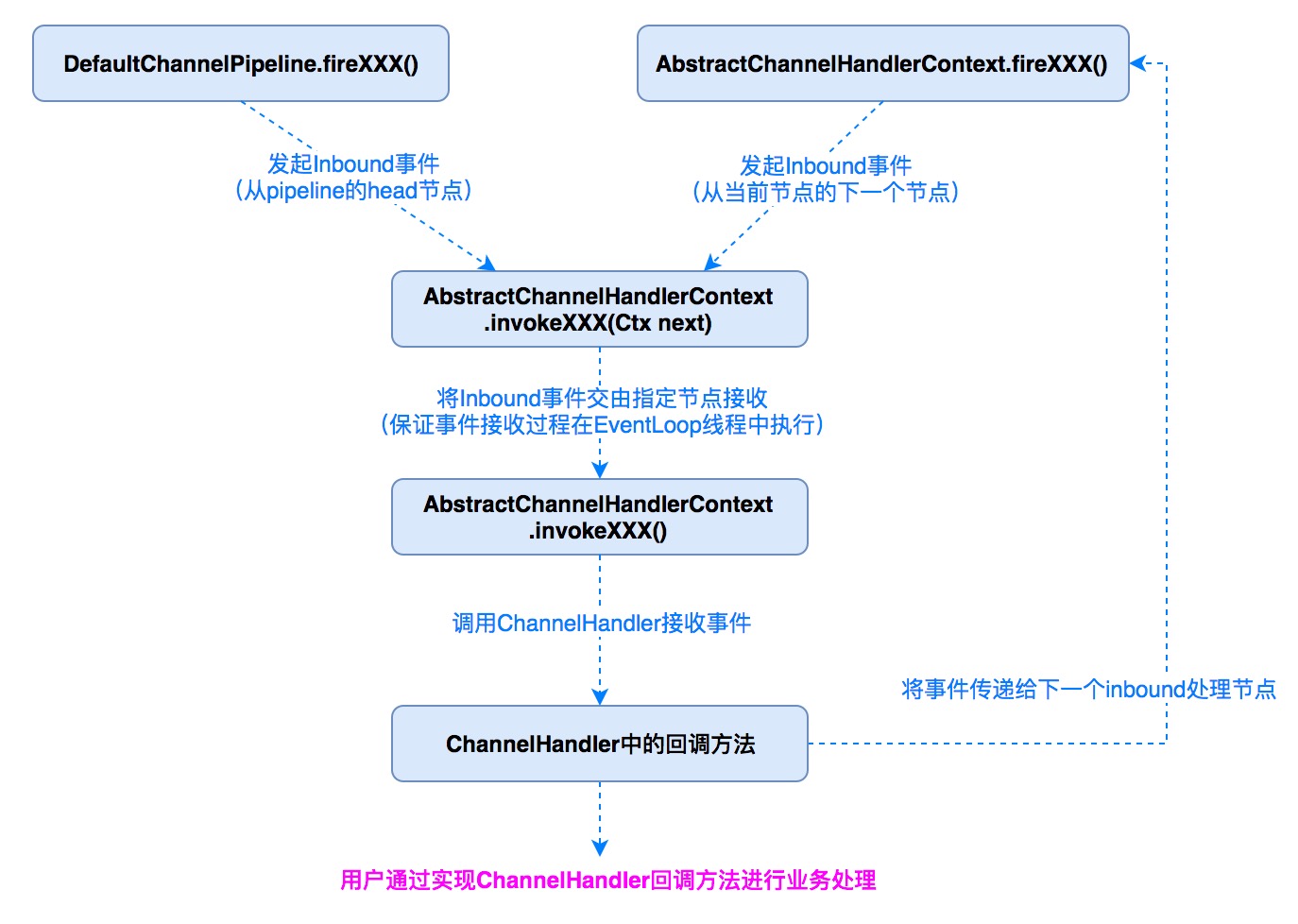
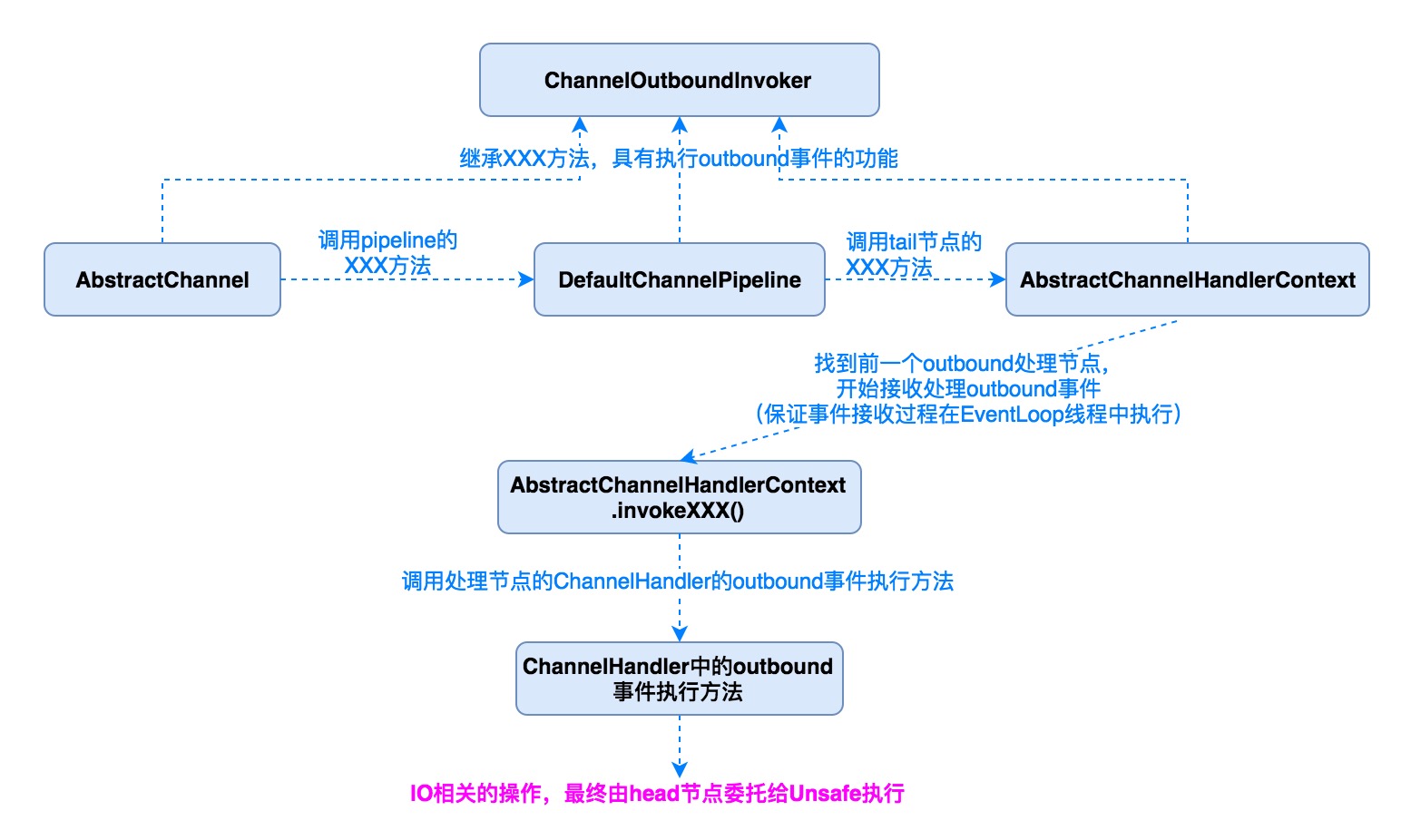
1.2 ChannelPipeline操作
1.2.1 自定拦截器
ChannelPipeline通过ChannelHandler接口来实现事件的拦截和处理,由于ChannelHandler中的事件种类繁多,不同的ChannelHandler可能只需要关心其中的某一个或者几个事件,所以,通常ChannelHandler只需要继承ChannelHandlerAdapter类覆盖自己关心的方法即可.
打印TCP链路建立成功日志
public class MyInboundHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
System.out.println("TCP connected!");
ctx.fireChannelActive();
}
}
链路关闭的时候释放资源
public class MyOutboundHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void close(ChannelHandlerContext ctx,ChannelPromise promise) {
System.out.println("TCP closing ...");
Object.release(promise);
ctx.close();
}
}
1.2.2 构建pipeline
事实上,用户不需要自己创建pipeline,因为使用ServerBootstrap或者Bootstrap启动服务端或者客户端时,Netty会为每个Channel连接创建一个独立的pipeline.对于使用者而言,只需要将自定义的拦截器加入到pipeline中即可.
pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast("decoder", new MyProtocolDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("encoder", new MyProtocolEncoder());
1.2.3 ChannelPipeline的主要特性
- ChannelPipeline支持运行态动态的添加或者删除ChannelHandler.
- ChannelPipeline是线程安全的,这意味着N个业务线程可以并发地操作ChannelPipeline而不存在多线程并发问题
- 注意: ChannelHandler却不是线程安全的,这意味着尽管ChannelPipeline是线程安全的,但是用户仍然需要自己保证ChannelHandler的线程安全
2.ChannelPipeline源码分析
2.1 继承图
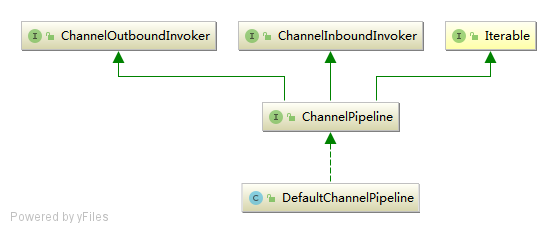
ChannelPipeline的代码相对比较简单,它实际上是一个ChannelHandler的容器,内部维护了一个ChannelHandler的链表和迭代器,可以方便地实现ChannelHandler查找、添加、替换和删除.
2.2 ChannelPipeline对ChannelHandler的管理
ChannelPipeline是ChannelHandler的管理容器,负责ChannelHandler的查询、添加、替换和删除,它与Map等容器的实现非常类似.
public class DefaultChannelPipeline implements ChannelPipeline {
@Override
public final ChannelPipeline addBefore(
EventExecutorGroup group, String baseName, String name, ChannelHandler handler) {
final AbstractChannelHandlerContext newCtx;
final AbstractChannelHandlerContext ctx;
// 保证线程的安全性
synchronized (this) {
// 对新增的ChannelHandler进行重复性校验
checkMultiplicity(handler);
name = filterName(name, handler);
ctx = getContextOrDie(baseName);
// 构造新的 DefaultChannelHandlerContext
newCtx = newContext(group, name, handler);
// 将新创建的DefaultChannelHandlerContext添加到当前的pipeline中
addBefore0(ctx, newCtx);
addBefore0(ctx, newCtx);
// If the registered is false it means that the channel was not registered on an eventloop yet.
// In this case we add the context to the pipeline and add a task that will call
// ChannelHandler.handlerAdded(...) once the channel is registered.
if (!registered) {
newCtx.setAddPending();
callHandlerCallbackLater(newCtx, true);
return this;
}
EventExecutor executor = newCtx.executor();
if (!executor.inEventLoop()) {
newCtx.setAddPending();
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
callHandlerAdded0(newCtx);
}
});
return this;
}
}
callHandlerAdded0(newCtx);
return this;
}
}
2.3 ChannelPipeline事件
public class DefaultChannelPipeline implements ChannelPipeline {
// ===== inbound事件 =====
@Override
public final ChannelPipeline fireChannelActive() {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext.invokeChannelActive(head);
return this;
}
@Override
public final ChannelPipeline fireChannelInactive() {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext.invokeChannelInactive(head);
return this;
}
@Override
public final ChannelPipeline fireExceptionCaught(Throwable cause) {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext.invokeExceptionCaught(head, cause);
return this;
}
@Override
public final ChannelPipeline fireUserEventTriggered(Object event) {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext.invokeUserEventTriggered(head, event);
return this;
}
@Override
public final ChannelPipeline fireChannelRead(Object msg) {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext.invokeChannelRead(head, msg);
return this;
}
@Override
public final ChannelPipeline fireChannelReadComplete() {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext.invokeChannelReadComplete(head);
return this;
}
@Override
public final ChannelPipeline fireChannelWritabilityChanged() {
AbstractChannelHandlerContext.invokeChannelWritabilityChanged(head);
return this;
}
// ===== outbound事件 =====
@Override
public final ChannelFuture bind(SocketAddress localAddress) {
return tail.bind(localAddress);
}
@Override
public final ChannelFuture connect(SocketAddress remoteAddress) {
return tail.connect(remoteAddress);
}
@Override
public final ChannelFuture connect(SocketAddress remoteAddress, SocketAddress localAddress) {
return tail.connect(remoteAddress, localAddress);
}
@Override
public final ChannelFuture disconnect() {
return tail.disconnect();
}
@Override
public final ChannelFuture close() {
return tail.close();
}
@Override
public final ChannelFuture deregister() {
return tail.deregister();
}
@Override
public final ChannelFuture bind(SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise) {
return tail.bind(localAddress, promise);
}
@Override
public final ChannelFuture connect(SocketAddress remoteAddress, ChannelPromise promise) {
return tail.connect(remoteAddress, promise);
}
@Override
public final ChannelFuture connect(
SocketAddress remoteAddress, SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise) {
return tail.connect(remoteAddress, localAddress, promise);
}
@Override
public final ChannelFuture disconnect(ChannelPromise promise) {
return tail.disconnect(promise);
}
@Override
public final ChannelFuture close(ChannelPromise promise) {
return tail.close(promise);
}
@Override
public final ChannelFuture deregister(final ChannelPromise promise) {
return tail.deregister(promise);
}
@Override
public final ChannelPipeline read() {
tail.read();
return this;
}
@Override
public final ChannelFuture write(Object msg) {
return tail.write(msg);
}
@Override
public final ChannelFuture write(Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) {
return tail.write(msg, promise);
}
@Override
public final ChannelFuture writeAndFlush(Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) {
return tail.writeAndFlush(msg, promise);
}
@Override
public final ChannelFuture writeAndFlush(Object msg) {
return tail.writeAndFlush(msg);
}
}
2.4 类的关系图
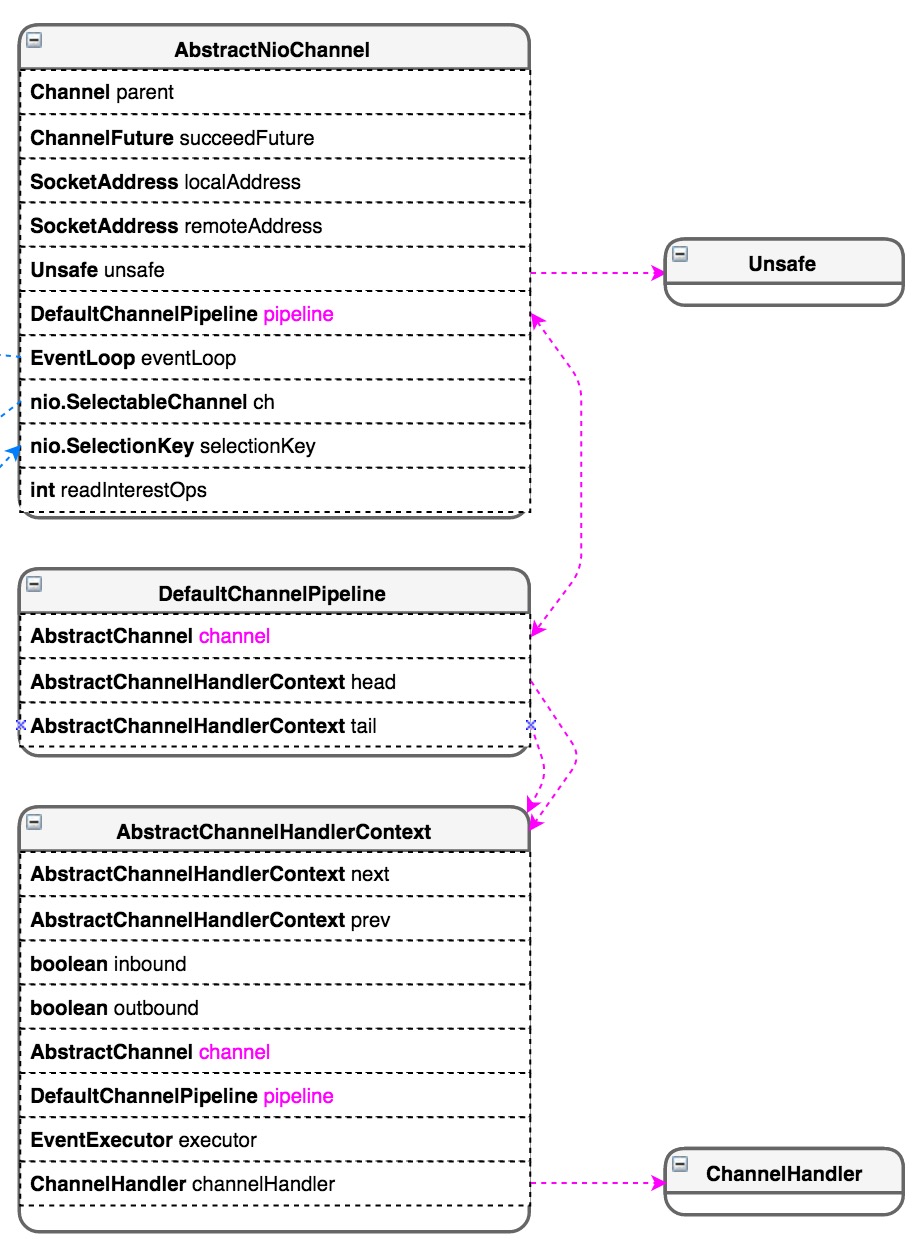
3.ChannelHandler
ChannelHandler支持的注解
Sharable:多个pipeline共用同一个ChannelHandlerSkip:被skip注解的方法不会调用,直接被忽略
3.1 ChannelHandlerAdapter
是ChannelHandler的实现类,用户只需要继承这些类,然后覆盖自己感兴趣的方法,不用直接实现ChannelHandler接口
3.2 Decoder和Encoder
- Decoder(解码器)
- ByteToMessageDecoder: 将ByteBuf解码成业务POJO对象
- 缺点: 没有考虑TCP粘包和组包等场景,读半包需要用户解码器自己负责处理,因此大多数场景不会直接继承,而是继承另外一些更高级的解码器
- MessageToMessageDecoder: 二次解码器, 将一个对象二次解码为其他对象
- SocketChannel读取TCP数据: ByteBuffer -> 解码为Java对象 -> 解码为业务POJO对象
- LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder: 半包解码器
- ByteToMessageDecoder: 将ByteBuf解码成业务POJO对象
- Encoder(编码器)
- MessageToByteEncoder: 将POJO对象解码成ByteBuf
- MessageToMessageEncoder: 将POJO对象编码成另一个对象, 再将字符串编码为HTTP请求或者应答消息
- LengthFieldPrepender: 计算当前待发送消息的二级制字节长度,将该长度添加到ByteBuf的缓存区头中
4.ChannelHandler源码分析
4.1 关系图
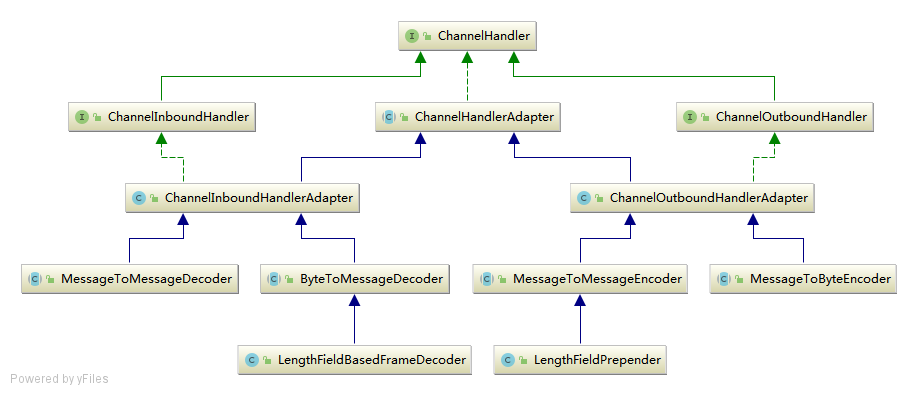
4.2 ChannelHandler
public interface ChannelHandler {
/**
* Gets called after the {@link ChannelHandler} was added to the actual context and it's ready to handle events.
*
* ChannelHandler 已经成功被添加到 ChannelPipeline 中,可以进行处理事件.
*
* 该方法,一般用于 ChannelHandler 的初始化的逻辑
*/
void handlerAdded(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception;
/**
* Gets called after the {@link ChannelHandler} was removed from the actual context and it doesn't handle events
* anymore.
*
* ChannelHandler 已经成功从 ChannelPipeline 中被移除,不再进行处理事件.
*
* 该方法,一般用于 ChannelHandler 的销毁的逻辑
*/
void handlerRemoved(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception;
/**
* Indicates that the same instance of the annotated {@link ChannelHandler}
* can be added to one or more {@link ChannelPipeline}s multiple times
* without a race condition.
* <p>
* If this annotation is not specified, you have to create a new handler
* instance every time you add it to a pipeline because it has unshared
* state such as member variables.
* <p>
* This annotation is provided for documentation purpose, just like
* <a href="http://www.javaconcurrencyinpractice.com/annotations/doc/">the JCIP annotations</a>.
*/
@Inherited
@Documented
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface Sharable {
// no value
}
}
4.3 Decoder和Encoder
4.3.1 Decoder
/**
* {@link ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter} which decodes bytes in a stream-like fashion from one {@link ByteBuf} to an
* other Message type.
*
* For example here is an implementation which reads all readable bytes from
* the input {@link ByteBuf} and create a new {@link ByteBuf}.
*
* <pre>
* public class SquareDecoder extends {@link ByteToMessageDecoder} {
* {@code @Override}
* public void decode({@link ChannelHandlerContext} ctx, {@link ByteBuf} in, List<Object> out)
* throws {@link Exception} {
* out.add(in.readBytes(in.readableBytes()));
* }
* }
* </pre>
*/
public abstract class ByteToMessageDecoder extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
if (msg instanceof ByteBuf) {
// 创建 CodecOutputList 对象
CodecOutputList out = CodecOutputList.newInstance();
try {
ByteBuf data = (ByteBuf) msg;
// 判断是否首次
first = cumulation == null;
// 若首次,直接使用读取的 data
if (first) {
cumulation = data;
// 若非首次,将读取的 data ,累积到 cumulation 中
} else {
cumulation = cumulator.cumulate(ctx.alloc(), cumulation, data);
}
// 执行解码
callDecode(ctx, cumulation, out);
} catch (DecoderException e) {
throw e; // 抛出异常
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new DecoderException(e); // 封装成 DecoderException 异常,抛出
} finally {
// cumulation 中所有数据被读取完,直接释放全部
if (cumulation != null && !cumulation.isReadable()) {
numReads = 0; // 重置 numReads 次数
cumulation.release(); // 释放 cumulation
cumulation = null; // 置空 cumulation
// 读取次数到达 discardAfterReads 上限,释放部分的已读
} else if (++ numReads >= discardAfterReads) {
// We did enough reads already try to discard some bytes so we not risk to see a OOME.
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/4275
numReads = 0; // 重置 numReads 次数
discardSomeReadBytes(); // 释放部分的已读
}
// 解码消息的数量
int size = out.size();
// 是否解码到消息
decodeWasNull = !out.insertSinceRecycled();
// 触发 Channel Read 事件.可能是多条消息
fireChannelRead(ctx, out, size);
// 回收 CodecOutputList 对象
out.recycle();
}
} else {
// 触发 Channel Read 事件
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);
}
}
}
public abstract class MessageToMessageDecoder<I> extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
// 创建 CodecOutputList 对象
CodecOutputList out = CodecOutputList.newInstance();
try {
// 判断是否为匹配的消息
if (acceptInboundMessage(msg)) {
// 转化消息类型
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
I cast = (I) msg;
try {
// 将消息解码成另外一个消息
decode(ctx, cast, out);
} finally {
// 释放 cast 原消息
ReferenceCountUtil.release(cast);
}
} else {
// 不匹配,添加到 out
out.add(msg);
}
} catch (DecoderException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new DecoderException(e);
} finally {
// 遍历 out ,触发 Channel Read 事件到 pipeline 中
int size = out.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i ++) {
ctx.fireChannelRead(out.getUnsafe(i));
}
// 回收 CodecOutputList 对象
out.recycle();
}
}
}
4.3.2 Encoder
/**
* {@link ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter} which encodes message in a stream-like fashion from one message to an
* {@link ByteBuf}.
*
*
* Example implementation which encodes {@link Integer}s to a {@link ByteBuf}.
*
* <pre>
* public class IntegerEncoder extends {@link MessageToByteEncoder}<{@link Integer}> {
* {@code @Override}
* public void encode({@link ChannelHandlerContext} ctx, {@link Integer} msg, {@link ByteBuf} out)
* throws {@link Exception} {
* out.writeInt(msg);
* }
* }
* </pre>
*/
public abstract class MessageToByteEncoder<I> extends ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = null;
try {
// 判断是否为匹配的消息
if (acceptOutboundMessage(msg)) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
I cast = (I) msg;
// 申请 buf
buf = allocateBuffer(ctx, cast, preferDirect);
// 编码
try {
encode(ctx, cast, buf);
} finally {
// 释放 msg
ReferenceCountUtil.release(cast);
}
// buf 可读,说明有编码到数据
if (buf.isReadable()) {
// 写入 buf 到下一个节点
ctx.write(buf, promise);
} else {
// 释放 buf
buf.release();
// 写入 EMPTY_BUFFER 到下一个节点,为了 promise 的回调
ctx.write(Unpooled.EMPTY_BUFFER, promise);
}
// 置空 buf
buf = null;
} else {
// 提交 write 事件给下一个节点
ctx.write(msg, promise);
}
} catch (EncoderException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new EncoderException(e);
} finally {
// 释放 buf
if (buf != null) {
buf.release();
}
}
}
}
/**
* {@link ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter} which encodes from one message to an other message
*
* For example here is an implementation which decodes an {@link Integer} to an {@link String}.
*
* <pre>
* public class IntegerToStringEncoder extends
* {@link MessageToMessageEncoder}<{@link Integer}> {
*
* {@code @Override}
* public void encode({@link ChannelHandlerContext} ctx, {@link Integer} message, List<Object> out)
* throws {@link Exception} {
* out.add(message.toString());
* }
* }
* </pre>
*
* Be aware that you need to call {@link ReferenceCounted#retain()} on messages that are just passed through if they
* are of type {@link ReferenceCounted}. This is needed as the {@link MessageToMessageEncoder} will call
* {@link ReferenceCounted#release()} on encoded messages.
*/
public abstract class MessageToMessageEncoder<I> extends ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
CodecOutputList out = null;
try {
// 判断是否为匹配的消息
if (acceptOutboundMessage(msg)) {
// 创建 CodecOutputList 对象
out = CodecOutputList.newInstance();
// 转化消息类型
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
I cast = (I) msg;
try {
// 将消息编码成另外一个消息
encode(ctx, cast, out);
} finally {
// 释放 cast 原消息
ReferenceCountUtil.release(cast);
}
// 如果未编码出消息,抛出异常
if (out.isEmpty()) {
// 回收 CodecOutputList 对象
out.recycle();
out = null;
// 抛出异常
throw new EncoderException(StringUtil.simpleClassName(this) + " must produce at least one message.");
}
} else {
// 直接下一个节点
ctx.write(msg, promise);
}
} catch (EncoderException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new EncoderException(t);
} finally {
if (out != null) {
final int sizeMinusOne = out.size() - 1;
// 只编码出一条消息
if (sizeMinusOne == 0) {
// 直接写入新消息到下一个节点
ctx.write(out.get(0), promise);
// 编码出多条消息
} else if (sizeMinusOne > 0) {
// 第 [0, n-1) 条消息,写入下一个节点,使用 voidPromise ,即不需要回调
// Check if we can use a voidPromise for our extra writes to reduce GC-Pressure
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2525
ChannelPromise voidPromise = ctx.voidPromise();
boolean isVoidPromise = promise == voidPromise;
for (int i = 0; i < sizeMinusOne; i ++) {
ChannelPromise p;
if (isVoidPromise) {
p = voidPromise;
} else {
p = ctx.newPromise();
}
ctx.write(out.getUnsafe(i), p);
}
// 第 n-1 条消息,写入下一个节点,使用 promise ,即需要回调
ctx.write(out.getUnsafe(sizeMinusOne), promise);
}
// 回收 CodecOutputList 对象
out.recycle();
}
}
}
}