Netty内存管理
1.简要
Netty内存池集大家之精华,参考了各路英雄豪杰的优秀思想,它参考了slab分配,Buddy分配.它的思路是把内存分割成大小不等的内存块,用户线程请求内存时根据请求的内存大小分配最贴近size的内存块,在减少内存碎片的同时又能很好的避免内存浪费.Buddy分配是在分配的过程中把一些内存块等量分割,回收时合并,尽可能保证系统中有足够大的连续内存.
1.1 JEMalloc分配算法
Netty的PooledByteBuf采用与jemalloc一致的内存分配算法.
1.1.1 jemalloc内存分配

1.1.2 Arena
为了提高内存分配效率并减少内部碎片,jemalloc算法将Arena切分为小块Chunk,根据每块的内存使用率又将小块组合为以下几种状态:QINIT,Q0,Q25,Q50,Q75,Q100.Chunk块可以在这几种状态间随着内存使用率的变化进行转移
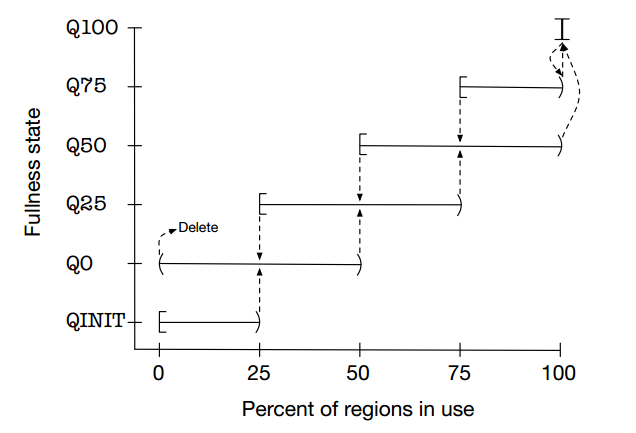
- QINIT的内存使用率为[0,25)、Q0为(0,50)、Q100为[100,100].
- Chunk块的初始状态为QINIT,当使用率达到25时转移到Q0状态,再次达到50时转移到Q25,依次类推直到Q100;当内存释放时又从Q100转移到Q75,直到Q0状态且内存使用率为0时,该Chunk从Arena中删除.注意极端情况下,Chunk可能从QINIT转移到Q0再释放全部内存,然后从Arena中删除.
1.1.3 Chunk和Page
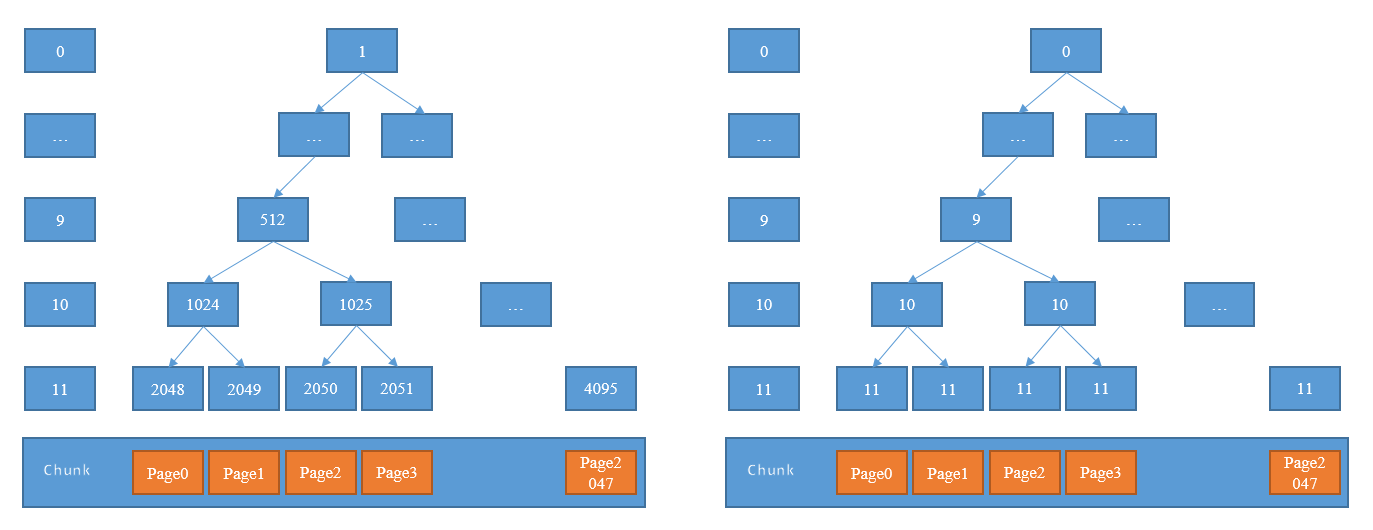
虽然已将Arena切分为小块Chunk,但实际上Chunk是相当大的内存块,在jemalloc中建议为4MB,Netty默认使用16MB.为了进一步提高内存利用率并减少内部碎片,需要继续将Chunk切分为小的块Page.一个典型的切分将Chunk切分为2048块,Netty正是如此,可知Page的大小为:16MB/2048=8KB.一个好的内存分配算法,应使得已分配内存块尽可能保持连续,这将大大减少内部碎片,由此jemalloc使用伙伴分配算法尽可能提高连续性.

图中最底层表示一个被切分为2048个Page的Chunk块.自底向上,每一层节点作为上一层的子节点构造出一棵满二叉树,然后按层分配满足要求的内存块.
以待分配序列8KB、16KB、8KB为例分析分配过程(每个Page大小8KB):
- 8KB -- 需要一个Page,第11层满足要求,故分配2048节点即Page0;
- 16KB -- 需要两个Page,故需要在第10层进行分配,而1024的子节点2048已分配,从左到右找到满足要求的1025节点,故分配节点1025即Page2和Page3;
- 8KB -- 需要一个Page,第11层满足要求,2048已分配,从左到右找到2049节点即Page1进行分配.
分配结束后,已分配连续的Page0-Page3,这样的连续内存块,大大减少内部碎片并提高内存使用率.
1.1.3 SubPage
Netty中每个Page的默认大小为8KB,在实际使用中,很多业务需要分配更小的内存块比如16B、32B、64B等.为了应对这种需求,需要进一步切分Page成更小的SubPage.SubPage是jemalloc中内存分配的最小单位,不能再进行切分.SubPage切分的单位并不固定,以第一次请求分配的大小为单位(最小切分单位为16B).比如,第一次请求分配32B,则Page按照32B均等切分为256块;第一次请求16B,则Page按照16B均等切分为512块.为了便于内存分配和管理,根据SubPage的切分单位进行分组,每组使用双向链表组合.
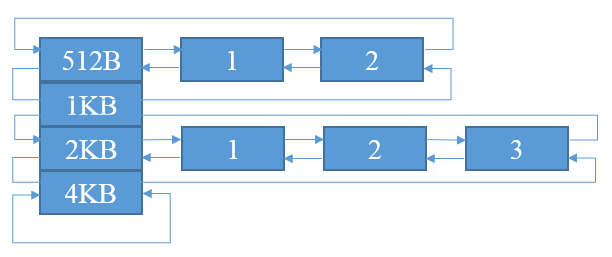
每组的头结点head只用来标记该组的大小,之后的节点才是实际分配的SubPage节点.
1.2 Netty内存模型
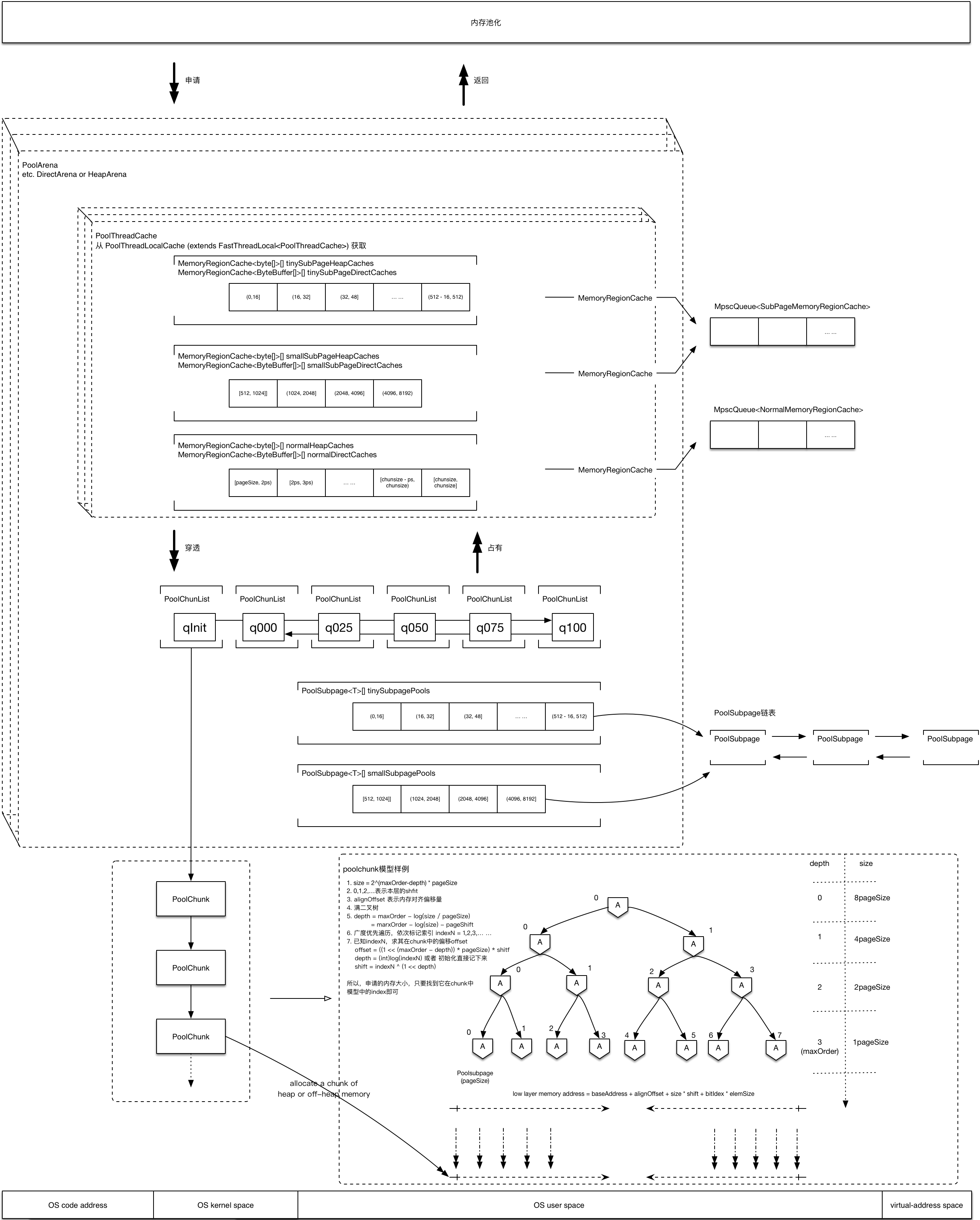
2.结构分析
netty内存池的层级结构,主要分为
PoolArenaChunkListChunkPageSubpage
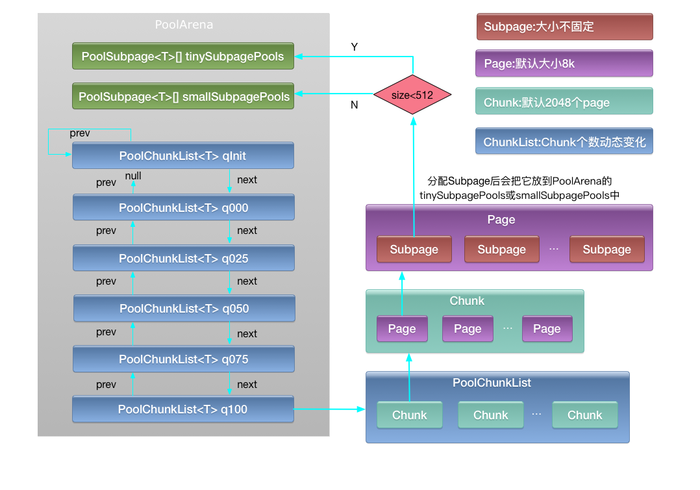
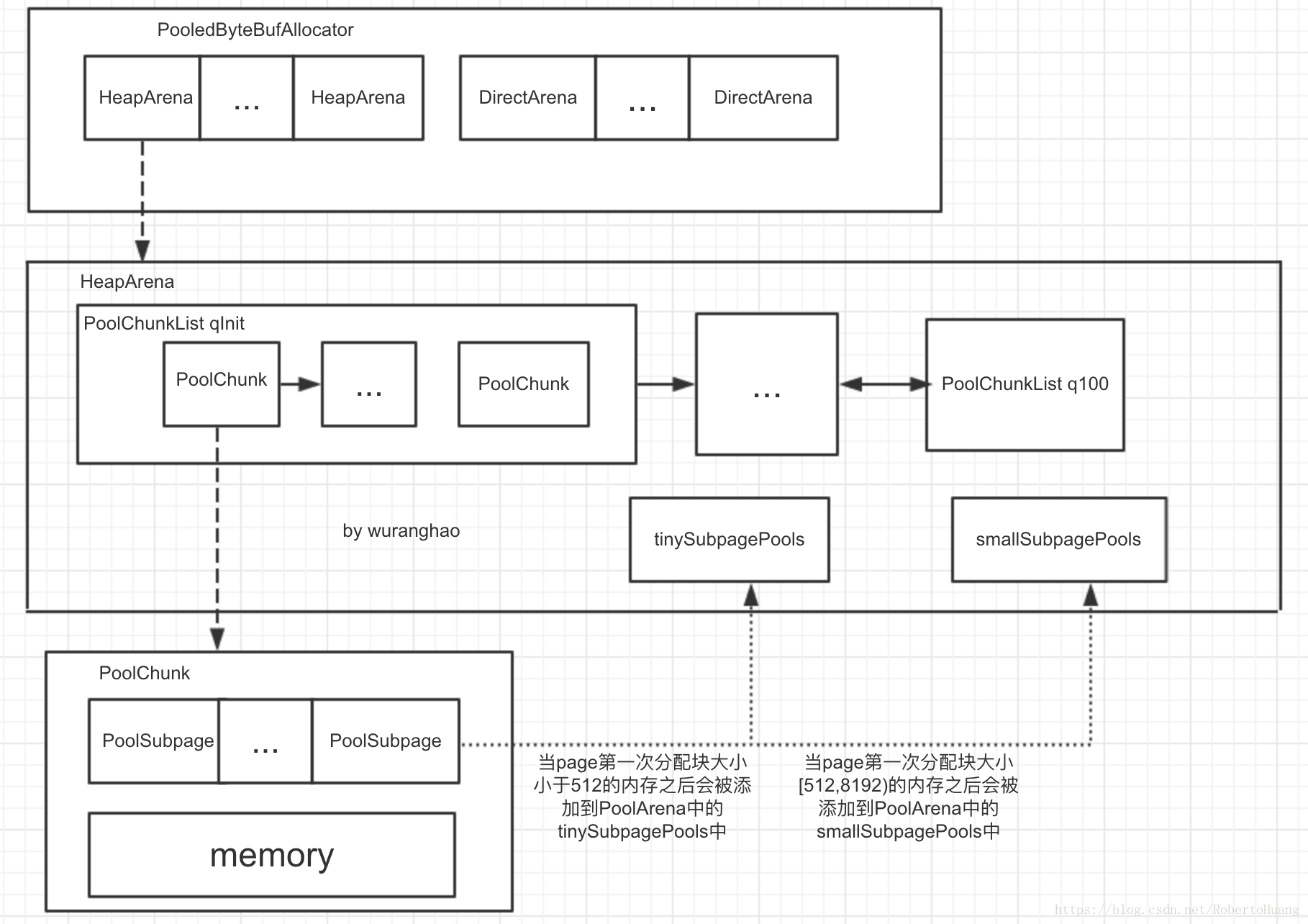
2.1 PoolArena

PoolArena,定义为管理那些jemalloc切分成chunks和底层pages的内存区域的一个结构
- 成员变量
abstract class PoolArena<T> implements PoolArenaMetric {
/**
* 是否支持 Unsafe 操作
*/
static final boolean HAS_UNSAFE = PlatformDependent.hasUnsafe();
/**
* 内存分类
*/
enum SizeClass {
Tiny,
Small,
Normal
// 还有一个隐藏的,Huge
}
/**
* {@link #tinySubpagePools} 数组的大小
*
* 默认为 32 .
*/
static final int numTinySubpagePools = 512 >>> 4;
/**
* 所属 PooledByteBufAllocator 对象
*/
final PooledByteBufAllocator parent;
/**
* 满二叉树的高度.默认为 11 .
*/
private final int maxOrder;
/**
* Page 大小,默认 8KB = 8192B
*/
final int pageSize;
/**
* 从 1 开始左移到 {@link #pageSize} 的位数.默认 13 ,1 << 13 = 8192 .
*/
final int pageShifts;
/**
* Chunk 内存块占用大小.默认为 16M = 16 * 1024 .
*/
final int chunkSize;
/**
* 判断分配请求内存是否为 Tiny/Small ,即分配 Subpage 内存块.
*
* Used to determine if the requested capacity is equal to or greater than pageSize.
*/
final int subpageOverflowMask;
/**
* {@link #smallSubpagePools} 数组的大小
*
* 默认为 4
*/
final int numSmallSubpagePools;
/**
* 对齐基准
*/
final int directMemoryCacheAlignment;
/**
* {@link #directMemoryCacheAlignment} 掩码
*/
final int directMemoryCacheAlignmentMask;
/**
* tiny 类型的 PoolSubpage 数组
*
* 数组的每个元素,都是双向链表
*/
private final PoolSubpage<T>[] tinySubpagePools;
/**
* small 类型的 SubpagePools 数组
*
* 数组的每个元素,都是双向链表
*/
private final PoolSubpage<T>[] smallSubpagePools;
// PoolChunkList 之间的双向链表
private final PoolChunkList<T> q050;
private final PoolChunkList<T> q025;
private final PoolChunkList<T> q000;
private final PoolChunkList<T> qInit;
private final PoolChunkList<T> q075;
private final PoolChunkList<T> q100;
/**
* PoolChunkListMetric 数组
*/
private final List<PoolChunkListMetric> chunkListMetrics;
// Metrics for allocations and deallocations
/**
* 分配 Normal 内存块的次数
*/
private long allocationsNormal;
// We need to use the LongCounter here as this is not guarded via synchronized block.
/**
* 分配 Tiny 内存块的次数
*/
private final LongCounter allocationsTiny = PlatformDependent.newLongCounter();
/**
* 分配 Small 内存块的次数
*/
private final LongCounter allocationsSmall = PlatformDependent.newLongCounter();
/**
* 分配 Huge 内存块的次数
*/
private final LongCounter allocationsHuge = PlatformDependent.newLongCounter();
/**
* 正在使用中的 Huge 内存块的总共占用字节数
*/
private final LongCounter activeBytesHuge = PlatformDependent.newLongCounter();
/**
* 释放 Tiny 内存块的次数
*/
private long deallocationsTiny;
/**
* 释放 Small 内存块的次数
*/
private long deallocationsSmall;
/**
* 释放 Normal 内存块的次数
*/
private long deallocationsNormal;
/**
* 释放 Huge 内存块的次数
*/
// We need to use the LongCounter here as this is not guarded via synchronized block.
private final LongCounter deallocationsHuge = PlatformDependent.newLongCounter();
/**
* 该 PoolArena 被多少线程引用的计数器
*/
// Number of thread caches backed by this arena.
final AtomicInteger numThreadCaches = new AtomicInteger();
// TODO: Test if adding padding helps under contention
//private long pad0, pad1, pad2, pad3, pad4, pad5, pad6, pad7;
protected PoolArena(PooledByteBufAllocator parent, int pageSize,
int maxOrder, int pageShifts, int chunkSize, int cacheAlignment) {
this.parent = parent;
this.pageSize = pageSize;
this.maxOrder = maxOrder;
this.pageShifts = pageShifts;
this.chunkSize = chunkSize;
directMemoryCacheAlignment = cacheAlignment;
directMemoryCacheAlignmentMask = cacheAlignment - 1;
subpageOverflowMask = ~(pageSize - 1);
// 初始化 tinySubpagePools 数组,固定为 512 >> 4 = 32
tinySubpagePools = newSubpagePoolArray(numTinySubpagePools);
for (int i = 0; i < tinySubpagePools.length; i ++) {
tinySubpagePools[i] = newSubpagePoolHead(pageSize); // 构造pools数组中的head元素
}
// 初始化 smallSubpagePools 数组,代表的是数组中每个元素之间增加一位的大小,如512,1024,2048,4096,...
numSmallSubpagePools = pageShifts - 9;
smallSubpagePools = newSubpagePoolArray(numSmallSubpagePools);
for (int i = 0; i < smallSubpagePools.length; i ++) {
smallSubpagePools[i] = newSubpagePoolHead(pageSize);
}
// PoolChunkList 之间的双向链表,初始化
// 构造链表 qInit -> q000 -> q025 -> q050 -> q075 -> q100
q100 = new PoolChunkList<T>(this, null, 100, Integer.MAX_VALUE, chunkSize); // 100%被使用
q075 = new PoolChunkList<T>(this, q100, 75, 100, chunkSize); // 75% ~ 100%被使用
q050 = new PoolChunkList<T>(this, q075, 50, 100, chunkSize); // 50% ~ 100%被使用
q025 = new PoolChunkList<T>(this, q050, 25, 75, chunkSize); // 25% ~ 75%被使用
q000 = new PoolChunkList<T>(this, q025, 1, 50, chunkSize); // 1% ~ 50%被使用
qInit = new PoolChunkList<T>(this, q000, Integer.MIN_VALUE, 25, chunkSize); // 0% ~ 25%被使用
// 构造链表 qInit <- qInit, q000 <- q025 <- q050 <- q075 <- q100
q100.prevList(q075);
q075.prevList(q050);
q050.prevList(q025);
q025.prevList(q000);
q000.prevList(null); // 无前置节点
qInit.prevList(qInit); // 前置节点为自己
// 创建 PoolChunkListMetric 数组(指标信息)
List<PoolChunkListMetric> metrics = new ArrayList<PoolChunkListMetric>(6);
metrics.add(qInit);
metrics.add(q000);
metrics.add(q025);
metrics.add(q050);
metrics.add(q075);
metrics.add(q100);
chunkListMetrics = Collections.unmodifiableList(metrics);
}
private PoolSubpage<T> newSubpagePoolHead(int pageSize) {
PoolSubpage<T> head = new PoolSubpage<T>(pageSize);
head.prev = head;
head.next = head;
return head;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private PoolSubpage<T>[] newSubpagePoolArray(int size) {
return new PoolSubpage[size];
}
}
申请内存
abstract class PoolArena<T> implements PoolArenaMetric { PooledByteBuf<T> allocate(PoolThreadCache cache, int reqCapacity, int maxCapacity) { // 创建 PooledByteBuf 对象 PooledByteBuf<T> buf = newByteBuf(maxCapacity); // 分配内存块给 PooledByteBuf 对象 allocate(cache, buf, reqCapacity); return buf; } private void allocate(PoolThreadCache cache, PooledByteBuf<T> buf, final int reqCapacity) { // 标准化请求分配的容量,根据大小移除锯齿 final int normCapacity = normalizeCapacity(reqCapacity); // PoolSubPage 的情况 if (isTinyOrSmall(normCapacity)) { // capacity < pageSize // 分配叶子节点的 int tableIdx; PoolSubpage<T>[] table; // 判断是否为 tiny 类型的内存块申请 boolean tiny = isTiny(normCapacity); if (tiny) { // < 512 tiny 类型的内存块申请 // 从 PoolThreadCache 缓存中,分配 tiny 内存块,并初始化到 PooledByteBuf 中. if (cache.allocateTiny(this, buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity)) { // was able to allocate out of the cache so move on return; } // 获得 tableIdx 和 table 属性 tableIdx = tinyIdx(normCapacity); // cache中没有,计算出申请大小在tinySubpagePools数组中的索引 table = tinySubpagePools; } else { // 从 PoolThreadCache 缓存中,分配 small 内存块,并初始化到 PooledByteBuf 中. if (cache.allocateSmall(this, buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity)) { // was able to allocate out of the cache so move on return; } // 获得 tableIdx 和 table 属性 tableIdx = smallIdx(normCapacity); // 计算申请大小在smallSubpagePools中的索引 table = smallSubpagePools; } // 获得 PoolSubpage 链表的头节点 final PoolSubpage<T> head = table[tableIdx]; // 从 PoolSubpage 链表中,分配 Subpage 内存块 /** * Synchronize on the head. This is needed as {@link PoolChunk#allocateSubpage(int)} and * {@link PoolChunk#free(long)} may modify the doubly linked list as well. */ synchronized (head) { // 同步 head ,避免并发问题 final PoolSubpage<T> s = head.next; if (s != head) { // 存在非head节点 assert s.doNotDestroy && s.elemSize == normCapacity; // 分配 Subpage 内存块 long handle = s.allocate(); assert handle >= 0; // 初始化 Subpage 内存块到 PooledByteBuf 对象中 s.chunk.initBufWithSubpage(buf, handle, reqCapacity); // 增加 allocationsTiny 或 allocationsSmall 计数 incTinySmallAllocation(tiny); // 返回,因为已经分配成功 return; } } // tiny or small subpage pools中没有可用subpage,意味着当前所有chunk里面没有碎片的subpage, 需要从chunk中重新分配一个叶子,然后进行拆分 // 拆分后的subpage又会根据其elementSize大小挂到subpage pools不同的位置 // 申请 Normal Page 内存块.实际上,只占用其中一块 Subpage 内存块. synchronized (this) { // 同步 arena ,避免并发问题 allocateNormal(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity); } // 增加 allocationsTiny 或 allocationsSmall 计数 incTinySmallAllocation(tiny); // 返回,因为已经分配成功 return; } if (normCapacity <= chunkSize) { // 如果申请的大小 大于subpage又小于chunksize,即为normal分配 // 从 PoolThreadCache 缓存中,分配 normal 内存块,并初始化到 PooledByteBuf 中. if (cache.allocateNormal(this, buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity)) { // was able to allocate out of the cache so move on return; } // 申请 Normal Page 内存块 synchronized (this) { // 同步 arena ,避免并发问题 allocateNormal(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity); // 增加 allocationsNormal ++allocationsNormal; } } else { // 申请 Huge Page 内存块 // Huge allocations are never served via the cache so just call allocateHuge allocateHuge(buf, reqCapacity); // 申请超过chunk size大小的的,则直接向系统申请,不进行池化 } } // tiny的为 0,16,32,48,... // small的为 512,1024,2048,4096,8192,... int normalizeCapacity(int reqCapacity) { if (reqCapacity < 0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("capacity: " + reqCapacity + " (expected: 0+)"); } // Huge 内存类型,直接使用 reqCapacity ,无需进行标准化. if (reqCapacity >= chunkSize) { return directMemoryCacheAlignment == 0 ? reqCapacity : alignCapacity(reqCapacity); } // 非 tiny 内存类型 if (!isTiny(reqCapacity)) { // >= 512 // 大于512并且小于chunk size即small subpage.大意为求reqCapacity对应2的次幂的值 // Doubled // 转换成接近于两倍的容量 int normalizedCapacity = reqCapacity; normalizedCapacity --; normalizedCapacity |= normalizedCapacity >>> 1; normalizedCapacity |= normalizedCapacity >>> 2; normalizedCapacity |= normalizedCapacity >>> 4; normalizedCapacity |= normalizedCapacity >>> 8; normalizedCapacity |= normalizedCapacity >>> 16; normalizedCapacity ++; if (normalizedCapacity < 0) { normalizedCapacity >>>= 1; } assert directMemoryCacheAlignment == 0 || (normalizedCapacity & directMemoryCacheAlignmentMask) == 0; return normalizedCapacity; } if (directMemoryCacheAlignment > 0) { return alignCapacity(reqCapacity); } // 补齐成 16 的倍数 // Quantum-spaced if ((reqCapacity & 15) == 0) { return reqCapacity; } return (reqCapacity & ~15) + 16; } // Method must be called inside synchronized(this) { ... } block // 必须在 synchronized(this) { ... } 中执行 private void allocateNormal(PooledByteBuf<T> buf, int reqCapacity, int normCapacity) { // 按照优先级,从多个 ChunkList 中,分配 Normal Page 内存块.如果有一分配成功,返回 // chunklist的查找逻辑是,先从q050开始查找,然后是q025, q000, qInit, q075 if (q050.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity) || q025.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity) || q000.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity) || qInit.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity) || q075.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity)) { return; } // Add a new chunk. // 新建 Chunk 内存块, 然后初始化这个chunk PoolChunk<T> c = newChunk(pageSize, maxOrder, pageShifts, chunkSize); // 申请对应的 Normal Page 内存块.实际上,如果申请分配的内存类型为 tiny 或 small 类型,实际申请的是 Subpage 内存块. long handle = c.allocate(normCapacity); assert handle > 0; // 初始化 Normal Page / Subpage 内存块到 PooledByteBuf 对象中 // 初始化地址信息,关联buf与内存块,然后buf的相关操作都是发生在指定的内存块内 c.initBuf(buf, handle, reqCapacity); // 添加到 ChunkList 双向链中. qInit.add(c); } // 分配大于chunk的内存,不进行池化 private void allocateHuge(PooledByteBuf<T> buf, int reqCapacity) { // 新建 Chunk 内存块,它是 unpooled 的 PoolChunk<T> chunk = newUnpooledChunk(reqCapacity); // 增加 activeBytesHuge activeBytesHuge.add(chunk.chunkSize()); // 初始化 Huge 内存块到 PooledByteBuf 对象中 buf.initUnpooled(chunk, reqCapacity); // 增加 allocationsHuge allocationsHuge.increment(); } }
2.2 ChunkList
| 状态 | 最小内存使用率 | 最大内存使用率 |
|---|---|---|
| QINIT | 1 | 25 |
| Q0 | 1 | 50 |
| Q25 | 25 | 75 |
| Q50 | 50 | 100 |
| Q75 | 75 | 100 |
| Q100 | 100 | 100 |
成员变量
final class PoolChunkList<T> implements PoolChunkListMetric { private static final Iterator<PoolChunkMetric> EMPTY_METRICS = Collections.<PoolChunkMetric>emptyList().iterator(); /** * 所属 PoolArena 对象 */ private final PoolArena<T> arena; /** * 下一个 PoolChunkList 对象 */ private final PoolChunkList<T> nextList; /** * Chunk 最小内存使用率 */ private final int minUsage; /** * Chunk 最大内存使用率 */ private final int maxUsage; /** * 每个 Chunk 最大可分配的容量 * * @see #calculateMaxCapacity(int, int) 方法 */ private final int maxCapacity; /** * PoolChunk 头节点 */ private PoolChunk<T> head; /** * 前一个 PoolChunkList 对象 */ // This is only update once when create the linked like list of PoolChunkList in PoolArena constructor. private PoolChunkList<T> prevList; // TODO: Test if adding padding helps under contention //private long pad0, pad1, pad2, pad3, pad4, pad5, pad6, pad7; PoolChunkList(PoolArena<T> arena, PoolChunkList<T> nextList, int minUsage, int maxUsage, int chunkSize) { assert minUsage <= maxUsage; this.arena = arena; this.nextList = nextList; this.minUsage = minUsage; this.maxUsage = maxUsage; // 计算 maxUsage 属性 maxCapacity = calculateMaxCapacity(minUsage, chunkSize); } /** * Calculates the maximum capacity of a buffer that will ever be possible to allocate out of the {@link PoolChunk}s * that belong to the {@link PoolChunkList} with the given {@code minUsage} and {@code maxUsage} settings. */ private static int calculateMaxCapacity(int minUsage, int chunkSize) { // 计算 minUsage 值 minUsage = minUsage0(minUsage); if (minUsage == 100) { // If the minUsage is 100 we can not allocate anything out of this list. return 0; } // Calculate the maximum amount of bytes that can be allocated from a PoolChunk in this PoolChunkList. // // As an example: // - If a PoolChunkList has minUsage == 25 we are allowed to allocate at most 75% of the chunkSize because // this is the maximum amount available in any PoolChunk in this PoolChunkList. return (int) (chunkSize * (100L - minUsage) / 100L); } }链表操作
final class PoolChunkList<T> implements PoolChunkListMetric {
void add(PoolChunk<T> chunk) {
// 超过当前 ChunkList 管理的 Chunk 的内存使用率上限,继续递归到下一个 ChunkList 节点进行添加.
if (chunk.usage() >= maxUsage) {
nextList.add(chunk);
return;
}
// 执行真正的添加
add0(chunk);
}
/**
* Adds the {@link PoolChunk} to this {@link PoolChunkList}.
*/
void add0(PoolChunk<T> chunk) {
chunk.parent = this;
// 无头节点,自己成为头节点
if (head == null) {
head = chunk;
chunk.prev = null;
chunk.next = null;
// 有头节点,自己成为头节点,原头节点成为自己的下一个节点
} else {
chunk.prev = null;
chunk.next = head;
head.prev = chunk;
head = chunk;
}
}
}
final class PoolChunkList<T> implements PoolChunkListMetric {
private void remove(PoolChunk<T> cur) {
// 当前节点为首节点,将下一个节点设置为头节点
if (cur == head) {
head = cur.next;
if (head != null) {
head.prev = null;
}
// 当前节点非首节点,将节点的上一个节点指向节点的下一个节点
} else {
PoolChunk<T> next = cur.next;
cur.prev.next = next;
if (next != null) {
next.prev = cur.prev;
}
}
}
}
final class PoolChunkList<T> implements PoolChunkListMetric {
private boolean move(PoolChunk<T> chunk) {
assert chunk.usage() < maxUsage;
// 小于当前 ChunkList 管理的 Chunk 的内存使用率下限,继续递归到上一个 ChunkList 节点进行添加.
if (chunk.usage() < minUsage) {
// Move the PoolChunk down the PoolChunkList linked-list.
return move0(chunk);
}
// 执行真正的添加
// PoolChunk fits into this PoolChunkList, adding it here.
add0(chunk);
return true;
}
/**
* Moves the {@link PoolChunk} down the {@link PoolChunkList} linked-list so it will end up in the right
* {@link PoolChunkList} that has the correct minUsage / maxUsage in respect to {@link PoolChunk#usage()}.
*/
private boolean move0(PoolChunk<T> chunk) {
// 无前置 ChunList 节点,移动失败
if (prevList == null) {
// 无前置节点时,PoolChunk 的内存使用率是 0 ,按照 Netty 目前的实践.
// There is no previous PoolChunkList so return false which result in having the PoolChunk destroyed and
// all memory associated with the PoolChunk will be released.
assert chunk.usage() == 0;
return false;
}
// 移动到前置节点
return prevList.move(chunk);
}
}
- 分配和释放
final class PoolChunkList<T> implements PoolChunkListMetric {
boolean allocate(PooledByteBuf<T> buf, int reqCapacity, int normCapacity) {
// 双向链表中无 Chunk
// 申请分配的内存超过 ChunkList 的每个 Chunk 最大可分配的容量
if (head == null || normCapacity > maxCapacity) {
// Either this PoolChunkList is empty or the requested capacity is larger then the capacity which can
// be handled by the PoolChunks that are contained in this PoolChunkList.
return false;
}
// 遍历双向链表,寻找满足需求的Chunk块.注意,遍历的是 ChunkList 的内部双向链表.
for (PoolChunk<T> cur = head;;) {
// 分配内存块
long handle = cur.allocate(normCapacity);
// 分配失败
if (handle < 0) {
// 进入下一节点
cur = cur.next;
// 若下一个节点不存在,返回 false ,结束循环
if (cur == null) {
return false; // 分配失败
}
// 分配成功
} else {
// 初始化内存块到 PooledByteBuf 对象中
cur.initBuf(buf, handle, reqCapacity);
// 超过当前 ChunkList 管理的 Chunk 的内存使用率上限
if (cur.usage() >= maxUsage) {
// 从当前 ChunkList 节点移除
remove(cur);
// 添加到下一个 ChunkList 节点
nextList.add(cur);
}
return true; // 分配成功
}
}
}
}
final class PoolChunkList<T> implements PoolChunkListMetric {
boolean free(PoolChunk<T> chunk, long handle) {
// 释放 PoolChunk 的指定位置( handle )的内存块
chunk.free(handle);
// 小于当前 ChunkList 管理的 Chunk 的内存使用率下限
if (chunk.usage() < minUsage) {
// 从当前 ChunkList 节点移除
remove(chunk);
// 添加到上一个 ChunkList 节点
// Move the PoolChunk down the PoolChunkList linked-list.
return move0(chunk);
}
// 释放成功
return true;
}
void destroy(PoolArena<T> arena) {
// 循环,销毁 ChunkList 管理的所有 Chunk
PoolChunk<T> chunk = head;
while (chunk != null) {
arena.destroyChunk(chunk);
chunk = chunk.next;
}
// 置空
head = null;
}
}
2.3 Chunk
2.3.1 netty实现的伙伴分配算法
Netty使用两个字节数组来表示两棵二叉树
memoryMap存放分配信息- 节点编号从1开始,省略0是因为这样更容易计算父子关系: 子节点加倍,父节点减半
- 节点上的数字作为数组索引即id
- 随着节点分配值改变
depthMap存放节点的高度信息- 节点编号从0开始
- 节点上的数字作为值
- 初始状态时,memoryMap和depthMap相等, 即
memoryMap[512] = depthMap[512] = 9 - 初始化后值不再改变
节点分配
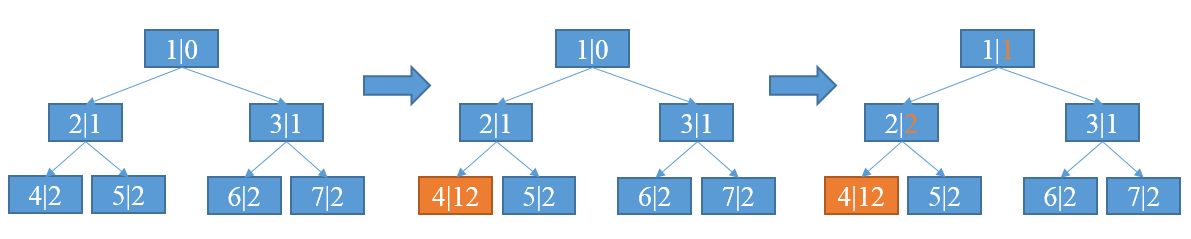
当一个节点被分配以后,该节点的值设置为12(最大高度+1)表示不可用,并且会更新祖先节点的值.
分配过程
- 每个节点的第一个数字表示节点编号,第二个数字表示节点高度值
- 4号节点被完全分配,将高度值设置为12表示不可用
- 4号节点的父亲节点即2号节点,将高度值更新为两个子节点的较小值;其他祖先节点亦然,直到高度值更新至根节点
memoryMap数组的值的三种情况
- memoryMap[id] = depthMap[id] -- 该节点没有被分配
- memoryMap[id] > depthMap[id] -- 至少有一个子节点被分配,不能再分配该高度满足的内存,但可以根据实际分配较小一些的内存.比如,上图中分配了4号子节点的2号节点,值从1更新为2,表示该节点不能再分配8MB的只能最大分配4MB内存,因为分配了4号节点后只剩下5号节点可用
- mempryMap[id] = 最大高度 + 1(本例中12) -- 该节点及其子节点已被完全分配, 没有剩余空间
2.3.2 源码分析
成员变量
final class PoolChunk<T> implements PoolChunkMetric { // ========== 关键成员变量 ========== /** * 分配信息满二叉树 * * index 为节点编号 */ private final byte[] memoryMap; /** * 高度信息满二叉树 * * index 为节点编号 */ private final byte[] depthMap; /** * PoolSubpage 数组 */ private final PoolSubpage<T>[] subpages; /** * 判断分配请求内存是否为 Tiny/Small ,即分配 Subpage 内存块. * * Used to determine if the requested capacity is equal to or greater than pageSize. */ private final int subpageOverflowMask; /** * Page 大小,默认 8KB = 8192B */ private final int pageSize; /** * 从 1 开始左移到 {@link #pageSize} 的位数.默认 13 ,1 << 13 = 8192 . * * 具体用途,见 {@link #allocateRun(int)} 方法,计算指定容量所在满二叉树的层级. */ private final int pageShifts; /** * 满二叉树的高度.默认为 11 . */ private final int maxOrder; /** * Chunk 内存块占用大小.默认为 16M = 16 * 1024 . */ private final int chunkSize; /** * log2 {@link #chunkSize} 的结果.默认为 log2( 16M ) = 24 . */ private final int log2ChunkSize; /** * 可分配 {@link #subpages} 的数量,即数组大小.默认为 1 << maxOrder = 1 << 11 = 2048 . */ private final int maxSubpageAllocs; /** * 标记节点不可用.默认为 maxOrder + 1 = 12 . * * Used to mark memory as unusable */ private final byte unusable; /** * 剩余可用字节数 */ private int freeBytes; // ========== 非关键成员变量 ========== /** * 所属 Arena 对象 */ final PoolArena<T> arena; /** * 内存空间. * * @see PooledByteBuf#memory */ final T memory; /** * 是否非池化 * * @see #PoolChunk(PoolArena, Object, int, int) 非池化.当申请的内存大小为 Huge 类型时,创建一整块 Chunk ,并且不拆分成若干 Page * @see #PoolChunk(PoolArena, Object, int, int, int, int, int) 池化 */ final boolean unpooled; final int offset; /** * 所属 PoolChunkList 对象 */ PoolChunkList<T> parent; /** * 上一个 Chunk 对象 */ PoolChunk<T> prev; /** * 下一个 Chunk 对象 */ PoolChunk<T> next; PoolChunk(PoolArena<T> arena, T memory, int pageSize, int maxOrder, int pageShifts, int chunkSize, int offset) { // 池化 unpooled = false; this.arena = arena; this.memory = memory; this.pageSize = pageSize; this.pageShifts = pageShifts; this.maxOrder = maxOrder; this.chunkSize = chunkSize; this.offset = offset; unusable = (byte) (maxOrder + 1); log2ChunkSize = log2(chunkSize); subpageOverflowMask = ~(pageSize - 1); freeBytes = chunkSize; assert maxOrder < 30 : "maxOrder should be < 30, but is: " + maxOrder; maxSubpageAllocs = 1 << maxOrder; // 初始化 memoryMap 和 depthMap // Generate the memory map. memoryMap = new byte[maxSubpageAllocs << 1]; depthMap = new byte[memoryMap.length]; int memoryMapIndex = 1; for (int d = 0; d <= maxOrder; ++ d) { // move down the tree one level at a time int depth = 1 << d; for (int p = 0; p < depth; ++ p) { // in each level traverse left to right and set value to the depth of subtree memoryMap[memoryMapIndex] = (byte) d; depthMap[memoryMapIndex] = (byte) d; memoryMapIndex ++; } } // 初始化 subpages subpages = newSubpageArray(maxSubpageAllocs); } /** Creates a special chunk that is not pooled. */ PoolChunk(PoolArena<T> arena, T memory, int size, int offset) { // 非池化(Huge分配请求) unpooled = true; this.arena = arena; this.memory = memory; this.offset = offset; memoryMap = null; depthMap = null; subpages = null; subpageOverflowMask = 0; pageSize = 0; pageShifts = 0; maxOrder = 0; unusable = (byte) (maxOrder + 1); chunkSize = size; log2ChunkSize = log2(chunkSize); maxSubpageAllocs = 0; } }分配
final class PoolChunk<T> implements PoolChunkMetric { long allocate(int normCapacity) { // 大于等于 Page 大小,分配 Page 内存块 if ((normCapacity & subpageOverflowMask) != 0) { // >= pageSize return allocateRun(normCapacity); // 小于 Page 大小,分配 Subpage 内存块,Tiny和Small请求 } else { return allocateSubpage(normCapacity); } }
以一个Page大小为8KB,pageShifts=13,maxOrder=11的配置为例分析分配32KB=2^15B内存的过程(假设该Chunk首次分配):
- 计算满足所需内存的高度d,d= maxOrder-(log2(normCapacity)-pageShifts) = 11-(log2(2^15)-13) = 9.可知,满足需求的节点的最大高度d = 9.
- 在高度<9的层从左到右寻找满足需求的节点.由于二叉树不便于按层遍历,故需要从根节点1开始遍历.本例中,找到id为512的节点,满足需求,将memory[512]设置为12表示分配.
- 从512节点开始,依次更新祖先节点的分配信息
final class PoolChunk<T> implements PoolChunkMetric {
/**
* Allocate a run of pages (>=1)
*
* @param normCapacity normalized capacity
* @return index in memoryMap
*/
private long allocateRun(int normCapacity) {
// 获得层级
int d = maxOrder - (log2(normCapacity) - pageShifts);
// 获得节点
int id = allocateNode(d);
// 未获得到节点,直接返回
if (id < 0) {
return id;
}
// 减少剩余可用字节数
freeBytes -= runLength(id);
return id;
}
/**
* Algorithm to allocate an index in memoryMap when we query for a free node
* at depth d
*
* @param d depth
* @return index in memoryMap
*/
private int allocateNode(int d) {
int id = 1;
int initial = - (1 << d); // has last d bits = 0 and rest all = 1
// 获得根节点的指值.
// 如果根节点的值,大于 d ,说明,第 d 层没有符合的节点,也就是说 [0, d-1] 层也没有符合的节点.即,当前 Chunk 没有符合的节点.
byte val = value(id);
if (val > d) { // unusable
return -1;
}
// 获得第 d 层,匹配的节点.
// id & initial 来保证,高度小于 d 会继续循环
while (val < d || (id & initial) == 0) { // id & initial == 1 << d for all ids at depth d, for < d it is 0
// 进入下一层
// 获得左节点的编号
id <<= 1;
// 获得左节点的值
val = value(id);
// 如果值大于 d ,说明,以左节点作为根节点形成虚拟的虚拟满二叉树,没有符合的节点.
if (val > d) {
// 获得右节点的编号
id ^= 1;
// 获得右节点的值
val = value(id);
}
}
// 校验获得的节点值合理
byte value = value(id);
assert value == d && (id & initial) == 1 << d : String.format("val = %d, id & initial = %d, d = %d",
value, id & initial, d);
// 更新获得的节点不可用
setValue(id, unusable); // mark as unusable
// 更新获得的节点的祖先都不可用
updateParentsAlloc(id);
// 返回节点编号
return id;
}
/**
* Update method used by allocate
* This is triggered only when a successor is allocated and all its predecessors
* need to update their state
* The minimal depth at which subtree rooted at id has some free space
*
* @param id id
*/
private void updateParentsAlloc(int id) {
while (id > 1) {
// 获得父节点的编号
int parentId = id >>> 1;
// 获得子节点的值
byte val1 = value(id);
// 获得另外一个子节点的
byte val2 = value(id ^ 1);
// 获得子节点较小值,并设置到父节点
byte val = val1 < val2 ? val1 : val2;
setValue(parentId, val);
// 跳到父节点
id = parentId;
}
}
}
由于Small/Tiny请求分配的内存小于PageSize,所以分配的节点必然在二叉树的最高层.找到最高层合适的节点后,新建或初始化subpage并加入到chunk的subpages数组,同时将subpage加入到arena的subpage双向链表中,最后完成分配请求的内存.
final class PoolChunk<T> implements PoolChunkMetric {
/**
* Create/ initialize a new PoolSubpage of normCapacity
* Any PoolSubpage created/ initialized here is added to subpage pool in the PoolArena that owns this PoolChunk
*
* @param normCapacity normalized capacity
* @return index in memoryMap
*/
private long allocateSubpage(int normCapacity) {
// 获得对应内存规格的 Subpage 双向链表的 head 节点
// Obtain the head of the PoolSubPage pool that is owned by the PoolArena and synchronize on it.
// This is need as we may add it back and so alter the linked-list structure.
PoolSubpage<T> head = arena.findSubpagePoolHead(normCapacity);
// 加锁,分配过程会修改双向链表的结构,会存在多线程的情况.
synchronized (head) {
// 获得最底层的一个节点.Subpage 只能使用二叉树的最底层的节点.
int d = maxOrder; // subpages are only be allocated from pages i.e., leaves
int id = allocateNode(d);
// 获取失败,直接返回
if (id < 0) {
return id;
}
final PoolSubpage<T>[] subpages = this.subpages;
final int pageSize = this.pageSize;
// 减少剩余可用字节数
freeBytes -= pageSize;
// 获得节点对应的 subpages 数组的编号
int subpageIdx = subpageIdx(id);
// 获得节点对应的 subpages 数组的 PoolSubpage 对象
PoolSubpage<T> subpage = subpages[subpageIdx];
// 初始化 PoolSubpage 对象
if (subpage == null) { // 不存在,则进行创建 PoolSubpage 对象
subpage = new PoolSubpage<T>(head, this, id, runOffset(id), pageSize, normCapacity);
subpages[subpageIdx] = subpage;
} else { // 存在,则重新初始化 PoolSubpage 对象
subpage.init(head, normCapacity);
}
// 分配 PoolSubpage 内存块
return subpage.allocate();
}
}
}
内存释放
final class PoolChunk<T> implements PoolChunkMetric { void free(long handle) { // 获得 memoryMap 数组的编号( 下标 ) int memoryMapIdx = memoryMapIdx(handle); // 获得 bitmap 数组的编号( 下标 ).注意,此时获得的还不是真正的 bitmapIdx 值,需要经过 `bitmapIdx & 0x3FFFFFFF` 运算. int bitmapIdx = bitmapIdx(handle); // 释放 Subpage begin ~ if (bitmapIdx != 0) { // free a subpage bitmapIdx 非空,说明释放的是 Subpage // 获得 PoolSubpage 对象 PoolSubpage<T> subpage = subpages[subpageIdx(memoryMapIdx)]; assert subpage != null && subpage.doNotDestroy; // 获得对应内存规格的 Subpage 双向链表的 head 节点 // Obtain the head of the PoolSubPage pool that is owned by the PoolArena and synchronize on it. // This is need as we may add it back and so alter the linked-list structure. PoolSubpage<T> head = arena.findSubpagePoolHead(subpage.elemSize); // 加锁,分配过程会修改双向链表的结构,会存在多线程的情况. synchronized (head) { // 释放 Subpage . if (subpage.free(head, bitmapIdx & 0x3FFFFFFF)) { return; } // ↑↑↑ 返回 false ,说明 Page 中无切分正在使用的 Subpage 内存块,所以可以继续向下执行,释放 Page } } // 释放 Page begin ~ // 增加剩余可用字节数 freeBytes += runLength(memoryMapIdx); // 设置 Page 对应的节点可用 setValue(memoryMapIdx, depth(memoryMapIdx)); // 更新 Page 对应的节点的祖先可用 updateParentsFree(memoryMapIdx); } private void updateParentsFree(int id) { // 获得当前节点的子节点的层级 int logChild = depth(id) + 1; while (id > 1) { // 获得父节点的编号 int parentId = id >>> 1; // 获得子节点的值 byte val1 = value(id); // 获得另外一个子节点的值 byte val2 = value(id ^ 1); // 获得当前节点的层级 logChild -= 1; // in first iteration equals log, subsequently reduce 1 from logChild as we traverse up // 两个子节点都可用,则直接设置父节点的层级 if (val1 == logChild && val2 == logChild) { setValue(parentId, (byte) (logChild - 1)); // 两个子节点任一不可用,则取子节点较小值,并设置到父节点 } else { byte val = val1 < val2 ? val1 : val2; setValue(parentId, val); } // 跳到父节点 id = parentId; } } }
2.4 Subpage
小于PageSize的分配请求执行过程
- 首次请求Arena分配,Arena中的双向链表为空,不能分配;传递给Chunk分配,Chunk找到一个空闲的Page,然后均等切分并加入到Arena链表中,最后分配满足要求的大小
- 之后请求分配同样大小的内存,则直接在Arena中的PoolSubpage双向链表进行分配;如果链表中的节点都没有空间分配,则重复第一步
Netty使用一个long整型表示在PoolSubpage中分配的结果,其中低32位表示PoolSubpage所属的Page的标号,高32位表示均等切分小块的块号.实际中,Netty使用位图来表示均等小块的分配信息,其中位图有用long数组表示,所以对于高32位,其中的低6位用来表示64位即一个long的分配信息,其余位用来表示long数组的索引
|<-- 24 -->| <-- 6 --> | <-- 32 --> |
| long数组偏移 | long的二进制位偏移| 所属Chunk标号 |
成员变量
final class PoolSubpage<T> implements PoolSubpageMetric { /** * 所属 PoolChunk 对象 */ final PoolChunk<T> chunk; /** * 在 {@link PoolChunk#memoryMap} 的节点编号 */ private final int memoryMapIdx; /** * 在 Chunk 中,偏移字节量 * * @see PoolChunk#runOffset(int) */ private final int runOffset; /** * Page 大小 {@link PoolChunk#pageSize} */ private final int pageSize; /** * Subpage 分配信息数组 * * 每个 long 的 bits 位代表一个 Subpage 是否分配. * 因为 PoolSubpage 可能会超过 64 个( long 的 bits 位数 ),所以使用数组. * 例如:Page 默认大小为 8KB ,Subpage 默认最小为 16 B ,所以一个 Page 最多可包含 8 * 1024 / 16 = 512 个 Subpage . * 因此,bitmap 数组大小为 512 / 64 = 8 . * 另外,bitmap 的数组大小,使用 {@link #bitmapLength} 来标记.或者说,bitmap 数组,默认按照 Subpage 的大小为 16B 来初始化. * 为什么是这样的设定呢?因为 PoolSubpage 可重用,通过 {@link #init(PoolSubpage, int)} 进行重新初始化. */ private final long[] bitmap; /** * 双向链表,前一个 PoolSubpage 对象 */ PoolSubpage<T> prev; /** * 双向链表,后一个 PoolSubpage 对象 */ PoolSubpage<T> next; /** * 是否未销毁 */ boolean doNotDestroy; /** * 每个 Subpage 的占用内存大小 */ int elemSize; /** * 总共 Subpage 的数量 */ private int maxNumElems; /** * {@link #bitmap} 长度 */ private int bitmapLength; /** * 下一个可分配 Subpage 的数组位置 */ private int nextAvail; /** * 剩余可用 Subpage 的数量 */ private int numAvail; // 双向链表,头节点 /** Special constructor that creates a linked list head */ PoolSubpage(int pageSize) { chunk = null; memoryMapIdx = -1; runOffset = -1; elemSize = -1; this.pageSize = pageSize; bitmap = null; } // 双向链表,Page 节点 PoolSubpage(PoolSubpage<T> head, PoolChunk<T> chunk, int memoryMapIdx, int runOffset, int pageSize, int elemSize) { this.chunk = chunk; this.memoryMapIdx = memoryMapIdx; this.runOffset = runOffset; this.pageSize = pageSize; // 创建 bitmap 数组,最小分配16(1>>>4)B所需的long(1>>>6)个数 bitmap = new long[pageSize >>> 10]; // pageSize / 16 / 64 // 初始化 init(head, elemSize); } void init(PoolSubpage<T> head, int elemSize) { // 未销毁 doNotDestroy = true; // 初始化 elemSize this.elemSize = elemSize; if (elemSize != 0) { // 初始化 maxNumElems maxNumElems = numAvail = pageSize / elemSize; // 初始化 nextAvail nextAvail = 0; // 计算 bitmapLength 的大小 bitmapLength = maxNumElems >>> 6; if ((maxNumElems & 63) != 0) { // 未整除,补 1. bitmapLength ++; } // 初始化 bitmap for (int i = 0; i < bitmapLength; i ++) { bitmap[i] = 0; } } // 添加到 Arena 的双向链表中. addToPool(head); } // 添加到 Arena 的双向链表中 private void addToPool(PoolSubpage<T> head) { assert prev == null && next == null; // 将当前节点,插入到 head 和 head.next 中间 prev = head; next = head.next; next.prev = this; head.next = this; } }分配
final class PoolSubpage<T> implements PoolSubpageMetric {
/**
* Returns the bitmap index of the subpage allocation.
*/
long allocate() {
// 防御性编程,不存在这种情况.
if (elemSize == 0) {
return toHandle(0);
}
// 可用数量为 0 ,或者已销毁,返回 -1 ,即不可分配.
if (numAvail == 0 || !doNotDestroy) {
return -1;
}
// 获得下一个可用的 Subpage 在 bitmap 中的总体位置
final int bitmapIdx = getNextAvail();
// 获得下一个可用的 Subpage 在 bitmap 中数组的位置, // 高24为表示long数组索引
int q = bitmapIdx >>> 6;
// 获得下一个可用的 Subpage 在 bitmap 中数组的位置的第几 bits, // 低6位表示在long中实际分配的二进制位
int r = bitmapIdx & 63;
assert (bitmap[q] >>> r & 1) == 0;
// 修改 Subpage 在 bitmap 中不可分配.
bitmap[q] |= 1L << r;
// 可用 Subpage 内存块的计数减一
if (-- numAvail == 0) { // 无可用 Subpage 内存块
// 从双向链表中移除
removeFromPool();
}
// 计算 handle
return toHandle(bitmapIdx);
}
private long toHandle(int bitmapIdx) {
return 0x4000000000000000L | (long) bitmapIdx << 32 | memoryMapIdx;
}
private int getNextAvail() {
int nextAvail = this.nextAvail;
// nextAvail 大于 0 ,意味着已经“缓存”好下一个可用的位置,直接返回即可.
if (nextAvail >= 0) {
this.nextAvail = -1;
return nextAvail;
}
// 寻找下一个 nextAvail
return findNextAvail();
}
private int findNextAvail() {
final long[] bitmap = this.bitmap;
final int bitmapLength = this.bitmapLength;
// 循环 bitmap
for (int i = 0; i < bitmapLength; i ++) {
long bits = bitmap[i];
// ~ 操作,如果不等于 0 ,说明有可用的 Subpage
if (~bits != 0) {
// 在这 bits 寻找可用 nextAvail
return findNextAvail0(i, bits);
}
}
// 未找到
return -1;
}
private int findNextAvail0(int i, long bits) {
final int maxNumElems = this.maxNumElems;
// 计算基础值,表示在 bitmap 的数组下标
final int baseVal = i << 6; // 相当于 * 64
// 遍历 64 bits
for (int j = 0; j < 64; j ++) {
// 计算当前 bit 是否未分配
if ((bits & 1) == 0) {
// 可能 bitmap 最后一个元素,并没有 64 位,通过 baseVal | j < maxNumElems 来保证不超过上限.
int val = baseVal | j;
if (val < maxNumElems) {
return val;
} else {
break;
}
}
// 去掉当前 bit
bits >>>= 1;
}
// 未找到
return -1;
}
}
释放
final class PoolSubpage<T> implements PoolSubpageMetric { boolean free(PoolSubpage<T> head, int bitmapIdx) { // 防御性编程,不存在这种情况. if (elemSize == 0) { return true; } // 获得 Subpage 在 bitmap 中数组的位置 int q = bitmapIdx >>> 6; // 获得 Subpage 在 bitmap 中数组的位置的第几 bits int r = bitmapIdx & 63; assert (bitmap[q] >>> r & 1) != 0; // 修改 Subpage 在 bitmap 中可分配. bitmap[q] ^= 1L << r; // 设置下一个可用为当前 Subpage setNextAvail(bitmapIdx); // 可用 Subpage 内存块的计数加一 if (numAvail ++ == 0) { // 添加到 Arena 的双向链表中. addToPool(head); return true; } // 还有 Subpage 在使用 if (numAvail != maxNumElems) { return true; // 没有 Subpage 在使用 } else { // 双向链表中,只有该节点,不进行移除 // Subpage not in use (numAvail == maxNumElems) if (prev == next) { // Do not remove if this subpage is the only one left in the pool. return true; } // 标记为已销毁 // Remove this subpage from the pool if there are other subpages left in the pool. doNotDestroy = false; // 从双向链表中移除 removeFromPool(); return false; } } }
2.5 PoolThreadCache
PoolThreadCache
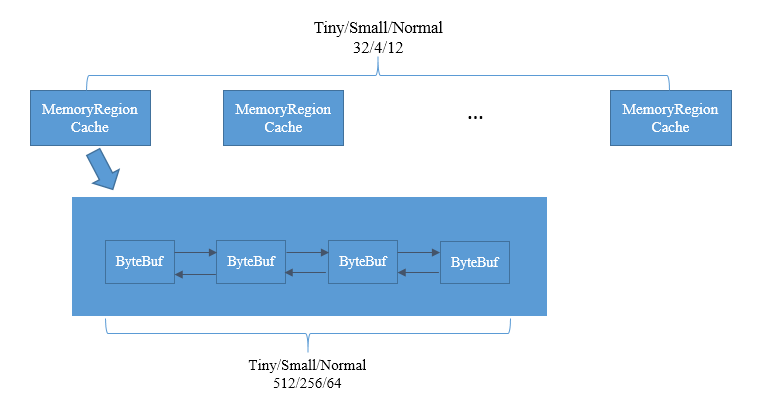
PoolThreadCache在Arena之上,释放内存的时候放入,申请内存的时候移出.顾名思义,就是Arena的一层缓存,为了减少同步控制,定义成了Threaded的.每个线程有自己的一个PoolThreadCache,互不干扰,向本线程内进行申请和释放都不需要同步控制.这个一个很重要的设计理念.
PoolThreadCache,内部维护了一系列数组,对应heap和off-heap,tiny和small、normal,数组的组织形式类似Arena中的subpage pools,也是一个元素一类大小,间隔根据一定递增,不过元素内部是一个MpscQueue,申请或者释放都通过这个queue完成.
需要特别说明的是,内存块的申请是发生在某个线程里面的,而内存块的释放也是发生在某个线程的,而这两个线程不一定是同一个.netty4的策略是,那个线程申请的内存块,释放的时候,就放回到对应的线程中.
数据类型MemoryRegionCache
其内部是一个ByteBuf队列.每个节点是一个ByteBuf的说法并不准确,切确的说,是不再使用的ByteBuf待释放的内存空间,可以再次使用这部分空间构建ByteBuf对象.根据分配请求大小的不同,MemoryRegionCache可以分为Tiny,Small,Normal三种.为了更方便的根据请求分配时的大小找到满足需求的缓存空间,每一种MemoryRegionCache又根据规范化后的大小依次组成数组,Tiny、Small、Normal的数组大小依次为32、4、12.其中ByteBuf队列的长度是有限制的,Tiny、Small、Normal依次为512、256、64.
| 分类 | 大小 |
|---|---|
| Tiny | 16B 32 ... 480B 496 |
| Small | 512B 1KB ... 2KB 4KB |
| Normal | 8KB 16KB ... 8MB 16MB |
| Huge | 32M 64M ... |
16B -- TinyCache[1] -- (Buf512-...-Buf3-Buf2-Buf1)
32B -- TinyCache[2] -- ()
496B -- TinyCache[31] -- (Buf2-Buf1)
512B -- SmallCache[0] -- (Buf256-...-Buf3-Buf2-Buf1)
8KB -- NormalCache[0] - (Buf64 -...-Buf3-Buf2-Buf1)
成员变量
final class PoolThreadCache { ** * 对应的 Heap PoolArena 对象 */ final PoolArena<byte[]> heapArena; /** * 对应的 Direct PoolArena 对象 */ final PoolArena<ByteBuffer> directArena; // Hold the caches for the different size classes, which are tiny, small and normal. /** * Heap 类型的 tiny Subpage 内存块缓存数组 */ private final MemoryRegionCache<byte[]>[] tinySubPageHeapCaches; /** * Heap 类型的 small Subpage 内存块缓存数组 */ private final MemoryRegionCache<byte[]>[] smallSubPageHeapCaches; /** * Heap 类型的 normal 内存块缓存数组 */ private final MemoryRegionCache<byte[]>[] normalHeapCaches; /** * Direct 类型的 tiny Subpage 内存块缓存数组 */ private final MemoryRegionCache<ByteBuffer>[] tinySubPageDirectCaches; /** * Direct 类型的 small Subpage 内存块缓存数组 */ private final MemoryRegionCache<ByteBuffer>[] smallSubPageDirectCaches; /** * Direct 类型的 normal 内存块缓存数组 */ private final MemoryRegionCache<ByteBuffer>[] normalDirectCaches; // Used for bitshifting when calculate the index of normal caches later /** * 用于计算请求分配的 normal 类型的内存块,在 {@link #normalDirectCaches} 数组中的位置 * * 默认为 log2(pageSize) = log2(8192) = 13 */ private final int numShiftsNormalDirect; /** * 用于计算请求分配的 normal 类型的内存块,在 {@link #normalHeapCaches} 数组中的位置 * * 默认为 log2(pageSize) = log2(8192) = 13 */ private final int numShiftsNormalHeap; /** * 分配次数 */ private int allocations; /** * {@link #allocations} 到达该阀值,释放缓存. * * 默认为 8192 次 * * @see #free() */ private final int freeSweepAllocationThreshold; PoolThreadCache(PoolArena<byte[]> heapArena, PoolArena<ByteBuffer> directArena, int tinyCacheSize, int smallCacheSize, int normalCacheSize, int maxCachedBufferCapacity, int freeSweepAllocationThreshold) { if (maxCachedBufferCapacity < 0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("maxCachedBufferCapacity: " + maxCachedBufferCapacity + " (expected: >= 0)"); } this.freeSweepAllocationThreshold = freeSweepAllocationThreshold; this.heapArena = heapArena; this.directArena = directArena; // 初始化 Direct 类型的内存块缓存 if (directArena != null) { // 创建 tinySubPageDirectCaches tinySubPageDirectCaches = createSubPageCaches(tinyCacheSize, PoolArena.numTinySubpagePools, SizeClass.Tiny); // 创建 smallSubPageDirectCaches smallSubPageDirectCaches = createSubPageCaches(smallCacheSize, directArena.numSmallSubpagePools, SizeClass.Small); // 计算 numShiftsNormalDirect numShiftsNormalDirect = log2(directArena.pageSize); // 创建 normalDirectCaches normalDirectCaches = createNormalCaches(normalCacheSize, maxCachedBufferCapacity, directArena); // 增加 directArena 的线程引用计数 directArena.numThreadCaches.getAndIncrement(); } else { // No directArea is configured so just null out all caches tinySubPageDirectCaches = null; smallSubPageDirectCaches = null; normalDirectCaches = null; numShiftsNormalDirect = -1; } // 初始化 Heap 类型的内存块缓存.同上面部分. if (heapArena != null) { // Create the caches for the heap allocations tinySubPageHeapCaches = createSubPageCaches(tinyCacheSize, PoolArena.numTinySubpagePools, SizeClass.Tiny); smallSubPageHeapCaches = createSubPageCaches(smallCacheSize, heapArena.numSmallSubpagePools, SizeClass.Small); numShiftsNormalHeap = log2(heapArena.pageSize); normalHeapCaches = createNormalCaches(normalCacheSize, maxCachedBufferCapacity, heapArena); heapArena.numThreadCaches.getAndIncrement(); } else { // No heapArea is configured so just null out all caches tinySubPageHeapCaches = null; smallSubPageHeapCaches = null; normalHeapCaches = null; numShiftsNormalHeap = -1; } // 校验参数,保证 PoolThreadCache 可缓存内存块. // Only check if there are caches in use. if ((tinySubPageDirectCaches != null || smallSubPageDirectCaches != null || normalDirectCaches != null || tinySubPageHeapCaches != null || smallSubPageHeapCaches != null || normalHeapCaches != null) && freeSweepAllocationThreshold < 1) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("freeSweepAllocationThreshold: " + freeSweepAllocationThreshold + " (expected: > 0)"); } } }创建Cache
final class PoolThreadCache {
// tiny 类型,默认 cacheSize = PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT_TINY_CACHE_SIZE = 512 , numCaches = PoolArena.numTinySubpagePools = 512 >>> 4 = 32
// small 类型,默认 cacheSize = PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT_SMALL_CACHE_SIZE = 256 , numCaches = pageSize - 9 = 13 - 9 = 4
private static <T> MemoryRegionCache<T>[] createSubPageCaches(int cacheSize, int numCaches, SizeClass sizeClass) {
if (cacheSize > 0 && numCaches > 0) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
MemoryRegionCache<T>[] cache = new MemoryRegionCache[numCaches];
for (int i = 0; i < cache.length; i++) {
// TODO: maybe use cacheSize / cache.length
cache[i] = new SubPageMemoryRegionCache<T>(cacheSize, sizeClass);
}
return cache;
} else {
return null;
}
}
// normal 类型,默认 cacheSize = PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT_NORMAL_CACHE_SIZE = 64 , maxCachedBufferCapacity = PoolArena.DEFAULT_MAX_CACHED_BUFFER_CAPACITY = 32 * 1024 = 32KB
private static <T> MemoryRegionCache<T>[] createNormalCaches(int cacheSize, int maxCachedBufferCapacity, PoolArena<T> area) {
if (cacheSize > 0 && maxCachedBufferCapacity > 0) {
// 计算数组大小
int max = Math.min(area.chunkSize, maxCachedBufferCapacity);
int arraySize = Math.max(1, log2(max / area.pageSize) + 1);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
MemoryRegionCache<T>[] cache = new MemoryRegionCache[arraySize];
for (int i = 0; i < cache.length; i++) {
cache[i] = new NormalMemoryRegionCache<T>(cacheSize);
}
return cache;
} else {
return null;
}
}
}
- 分配释放
final class PoolThreadCache {
@SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" })
private boolean allocate(MemoryRegionCache<?> cache, PooledByteBuf buf, int reqCapacity) {
if (cache == null) {
// no cache found so just return false here
return false;
}
// 分配内存块,并初始化到 MemoryRegionCache 中
boolean allocated = cache.allocate(buf, reqCapacity);
// 到达阀值,整理缓存
if (++ allocations >= freeSweepAllocationThreshold) {
allocations = 0;
trim();
}
// 返回是否分配成功
return allocated;
}
void free() {
// 清空缓存
int numFreed = free(tinySubPageDirectCaches) +
free(smallSubPageDirectCaches) +
free(normalDirectCaches) +
free(tinySubPageHeapCaches) +
free(smallSubPageHeapCaches) +
free(normalHeapCaches);
if (numFreed > 0 && logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Freed {} thread-local buffer(s) from thread: {}", numFreed, Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
// 减小 directArena 的线程引用计数
if (directArena != null) {
directArena.numThreadCaches.getAndDecrement();
}
// 减小 heapArena 的线程引用计数
if (heapArena != null) {
heapArena.numThreadCaches.getAndDecrement();
}
}
private static int free(MemoryRegionCache<?>[] caches) {
if (caches == null) {
return 0;
}
int numFreed = 0;
for (MemoryRegionCache<?> c: caches) {
numFreed += free(c);
}
return numFreed;
}
}
MemoryRegionCache
final class PoolThreadCache { private abstract static class MemoryRegionCache<T> { /** * {@link #queue} 队列大小 */ private final int size; /** * 队列.里面存储内存块 */ private final Queue<Entry<T>> queue; /** * 内存类型 */ private final SizeClass sizeClass; /** * 分配次数计数器 */ private int allocations; MemoryRegionCache(int size, SizeClass sizeClass) { this.size = MathUtil.safeFindNextPositivePowerOfTwo(size); queue = PlatformDependent.newFixedMpscQueue(this.size); // MPSC this.sizeClass = sizeClass; } /** * Init the {@link PooledByteBuf} using the provided chunk and handle with the capacity restrictions. */ protected abstract void initBuf(PoolChunk<T> chunk, long handle, PooledByteBuf<T> buf, int reqCapacity); /** * Add to cache if not already full. */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public final boolean add(PoolChunk<T> chunk, long handle) { // 创建 Entry 对象 Entry<T> entry = newEntry(chunk, handle); // 添加到队列 boolean queued = queue.offer(entry); // 若添加失败,说明队列已满,回收 Entry 对象 if (!queued) { // If it was not possible to cache the chunk, immediately recycle the entry entry.recycle(); } return queued; // 是否添加成功 } /** * Allocate something out of the cache if possible and remove the entry from the cache. */ public final boolean allocate(PooledByteBuf<T> buf, int reqCapacity) { // 获取并移除队列首个 Entry 对象 Entry<T> entry = queue.poll(); // 获取失败,返回 false if (entry == null) { return false; } // 初始化内存块到 PooledByteBuf 对象中 initBuf(entry.chunk, entry.handle, buf, reqCapacity); // 回收 Entry 对象 entry.recycle(); // 增加 allocations 计数.因为分配总是在相同线程,所以不需要考虑线程安全的问题 // allocations is not thread-safe which is fine as this is only called from the same thread all time. ++ allocations; return true; // 返回 true ,分配成功 } /** * 清除队列中的全部 * * Clear out this cache and free up all previous cached {@link PoolChunk}s and {@code handle}s. */ public final int free() { return free(Integer.MAX_VALUE); } // 清除队列中的指定数量元素 private int free(int max) { int numFreed = 0; for (; numFreed < max; numFreed++) { // 获取并移除首元素 Entry<T> entry = queue.poll(); if (entry != null) { // 释放缓存的内存块回 Chunk 中 freeEntry(entry); } else { // all cleared return numFreed; } } return numFreed; } /** * Free up cached {@link PoolChunk}s if not allocated frequently enough. */ public final void trim() { // allocations 表示已经重新分配出去的ByteBuf个数 int free = size - allocations; allocations = 0; // 在一定阈值内还没被分配出去的空间将被释放 // We not even allocated all the number that are if (free > 0) { free(free); // 释放队列中的节点 } } @SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" }) private void freeEntry(Entry entry) { PoolChunk chunk = entry.chunk; long handle = entry.handle; // 回收 Entry 对象 // recycle now so PoolChunk can be GC'ed. entry.recycle(); // 释放缓存的内存块回 Chunk 中 chunk.arena.freeChunk(chunk, handle, sizeClass); } static final class Entry<T> { /** * Recycler 处理器,用于回收 Entry 对象 */ final Handle<Entry<?>> recyclerHandle; /** * PoolChunk 对象 */ PoolChunk<T> chunk; /** * 内存块在 {@link #chunk} 的位置 */ long handle = -1; Entry(Handle<Entry<?>> recyclerHandle) { this.recyclerHandle = recyclerHandle; } void recycle() { // 置空 chunk = null; handle = -1; // 回收 Entry 对象 recyclerHandle.recycle(this); } } @SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") private static Entry newEntry(PoolChunk<?> chunk, long handle) { // 从 Recycler 对象中,获得 Entry 对象 Entry entry = RECYCLER.get(); // 初始化属性 entry.chunk = chunk; entry.handle = handle; return entry; } @SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") private static final Recycler<Entry> RECYCLER = new Recycler<Entry>() { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") @Override protected Entry newObject(Handle<Entry> handle) { return new Entry(handle); // 创建 Entry 对象 } }; } }
2.6 PoolThreadLocalCache
PoolThreadLocalCache,是实现PoolThreadCache线程私有的核心类.该类,本质上同JAVA中的ThreadLocal,虽然功能相同,但是实现不同.ThreadLocal是通过map进行查找的,比较低效,原因其一为需要进行hash计算,其二内部通过Entry table[]数组的结构存储数据,然后拿Thread的固定hash进行进行has查找,一个hash冲突的概率很大,二则table长度是会发生变化的,一旦发生变化,就需block进行重新哈希,重新构造table.特别是在线程不确定的时候,会频繁rehash和resize,效率能高到哪去.
netty4实现的版本,之所以命名为FastThreadLocal,就是解决了上述问题(resize没有解决),一不通过hash的方式而是通过数组索引的方式查找元素,二是优化了使用不需要主动remove(ThreadLocal中如果不remove会造成内存泄漏)
获取
public class FastThreadLocal<V> { private final int index; public FastThreadLocal() { index = InternalThreadLocalMap.nextVariableIndex(); } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public final V get() { InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = InternalThreadLocalMap.get(); Object v = threadLocalMap.indexedVariable(index); if (v != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) { return (V) v; } V value = initialize(threadLocalMap); registerCleaner(threadLocalMap); return value; } private void registerCleaner(final InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap) { Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); if (FastThreadLocalThread.willCleanupFastThreadLocals(current) || threadLocalMap.indexedVariable(cleanerFlagIndex) != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) { return; } // removeIndexedVariable(cleanerFlagIndex) isn't necessary because the finally cleanup is tied to the lifetime // of the thread, and this Object will be discarded if the associated thread is GCed. threadLocalMap.setIndexedVariable(cleanerFlagIndex, Boolean.TRUE); // We will need to ensure we will trigger remove(InternalThreadLocalMap) so everything will be released // and FastThreadLocal.onRemoval(...) will be called. ObjectCleaner.register(current, new Runnable() { // 注册 @Override public void run() { remove(threadLocalMap); // FastThreadLocal的清扫任务 // It's fine to not call InternalThreadLocalMap.remove() here as this will only be triggered once // the Thread is collected by GC. In this case the ThreadLocal will be gone away already. } }); } }自动回收
public final class ObjectCleaner { private static final Runnable CLEANER_TASK = new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { boolean interrupted = false; for (;;) { // Keep on processing as long as the LIVE_SET is not empty and once it becomes empty // See if we can let this thread complete. while (!LIVE_SET.isEmpty()) { final AutomaticCleanerReference reference; try { reference = (AutomaticCleanerReference) REFERENCE_QUEUE.remove(REFERENCE_QUEUE_POLL_TIMEOUT_MS); } catch (InterruptedException ex) { // Just consume and move on interrupted = true; continue; } if (reference != null) { try { reference.cleanup(); } catch (Throwable ignored) { // ignore exceptions, and don't log in case the logger throws an exception, blocks, or has // other unexpected side effects. } LIVE_SET.remove(reference); } } CLEANER_RUNNING.set(false); // Its important to first access the LIVE_SET and then CLEANER_RUNNING to ensure correct // behavior in multi-threaded environments. if (LIVE_SET.isEmpty() || !CLEANER_RUNNING.compareAndSet(false, true)) { // There was nothing added after we set STARTED to false or some other cleanup Thread // was started already so its safe to let this Thread complete now. break; } } if (interrupted) { // As we caught the InterruptedException above we should mark the Thread as interrupted. Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); } } }; public static void register(Object object, Runnable cleanupTask) { AutomaticCleanerReference reference = new AutomaticCleanerReference(object, ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(cleanupTask, "cleanupTask")); // Its important to add the reference to the LIVE_SET before we access CLEANER_RUNNING to ensure correct // behavior in multi-threaded environments. LIVE_SET.add(reference); // Check if there is already a cleaner running. if (CLEANER_RUNNING.compareAndSet(false, true)) { final Thread cleanupThread = new FastThreadLocalThread(CLEANER_TASK); cleanupThread.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY); // Set to null to ensure we not create classloader leaks by holding a strong reference to the inherited // classloader. // See: // - https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/7290 // - https://bugs.openjdk.java.net/browse/JDK-7008595 AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Void>() { @Override public Void run() { cleanupThread.setContextClassLoader(null); return null; } }); cleanupThread.setName(CLEANER_THREAD_NAME); // Mark this as a daemon thread to ensure that we the JVM can exit if this is the only thread that is // running. cleanupThread.setDaemon(true); cleanupThread.start(); } } }
AutomaticCleanerReference是一个弱引用,引用对象是Thread,意味着,如果JVM发现该对象只有弱引用引用的时候,该弱引用就会被加入到一个公共的ReferenceQueue队列里面.这个队列由一个清扫线程CLEANER_TASK进行阻塞remove操作,一旦队列里面有值,就会调用清扫任务进行清扫.
这里有必要分析一下可能会产生内存泄漏的情况,netty的表现会是什么:
- FastThreadLocal本身被GC,但是FastThreadLocalThread并没有退出
- 这种情况下,FastThreadLocal关联的对象仍然被FastThreadLocalThread中的InternalThreadLocalMap持有强引用(Object[]数组中).这个对象是不会被GC的,会造成内存泄漏.自动清扫功能是弱引用的Thread,只有thread被gc的时候才会触发自动清扫.
- FastThreadLocalThread退出,但是FastThreadLocal没有销毁比如static修饰
- 线程退出,就会触发自动清扫,FastThreadLocal并不持有InternalThreadMap的引用
- FastThreadLocalThread和FastThreadLocal都被销毁了
- 这种情况,在一些热更新系统里面,如果不设置清扫线程的classloader为null会造成classloader内存泄漏,netty已经解决,所以不会内存泄漏
- FastThreadLocal关联的对象在netty中,通常是Buf,如果Thread退出,LocalMap也会被销毁,但是关联的Buf怎么销毁
- 清扫线程提供了一个外放的清扫Runnable,注册清扫的时候关联上这个Runnable,就可以实现对FastThreadLocal关联对象的清扫,比如内存释放或回收
- netty4还提供了一种自动检测功能,详见下文
通过分析可以知道,FastThreadLocal确实比ThreadLocal要更优,但是为了避免内存泄漏,需要注意以下几点:
- FastThreadLocal的自动清扫是关联Thread的生命周期的,如果Thread是一个永不销毁的线程,就必须手动进行释放
- 自动清扫功能仅仅是触发一个时机而已,实际的回收逻辑需要实现
3.内存结构总结
4.netty内存池可调优参数
| 参数名 | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
| io.netty.allocator.pageSize | page的大小 | 8192 |
| io.netty.allocator.maxOrder | 一个chunk的大小=pageSize << maxOrder | 11 |
| io.netty.allocator.numHeapArenas | heap arena的个数 | min(cpu核数,maxMemory/chunkSize/6),一般来说会=cpu核数 |
| io.netty.allocator.numDirectArenas | direct arena的个数 | min(cpu核数,directMemory/chunkSize/6),一般来说会=cpu核数 |
| io.netty.allocator.tinyCacheSize | PoolThreadCache中tiny cache每个MemoryRegionCache中的Entry个数 | 512 |
| io.netty.allocator.smallCacheSize | PoolThreadCache中small cache每个MemoryRegionCache中的Entry个数 | 256 |
| io.netty.allocator.normalCacheSize | PoolThreadCache中normal cache每个MemoryRegionCache中的Entry个数 | 64 |
| io.netty.allocator.maxCachedBufferCapacity | PoolThreadCache中normal cache数组长度 | 32 * 1024 |
| io.netty.allocator.cacheTrimInterval | PoolThreadCache中的cache收缩阈值,每隔该值次数,会进行一次收缩 | 8192 |
| io.netty.allocator.type | allocator类型,如果不使用内存池,则设置为unpooled | pooled |
| io.netty.noUnsafe | 是否关闭direct buffer | false |
| io.netty.leakDetectionLevel | 内存泄露检测级别 | SIMPLE |