ByteBuf
1.ByteBuf和相关辅助类
1.1 对比
- ByteBuffer的缺点
- ByteBuffer长度固定,一旦分配完成,它的容量不能动态扩展和收敛
- 只有一个标志位置的指针position,需要手动调用flip
- API功能受限,一些高级和实用的特性不支持
- ByteBuf的特点
- 缓冲区自身的copy和slice
- ByteBuf通过两个位置指针来协助缓冲区的读写操作,读操作使用readerIndex,写操作使用writerIndex.
- readerIndex和writerIndex一开始是0
- 随着读的增加,readerIndex会递增,随着写的增加,writerIndex会递增,但是readerIndex不会超过writerIndex
- 读取之后,0-readerIndex就被视为discard,调用discardReadBytes可以释放这部分空间
- writerIndex-capacity之间的空间是可以写的
- ByteBuf可以动态扩展.ByteBuffer为了防止溢出,每进行一次put操作,都需要对可用空间进行校验,这导致代码冗余.ByteBuf对write操作进行了封装,有ByteBuf的write操作负责进行剩余可用空间校验,如果缓冲区不够会自动扩展
1.2 ByteBuf执行过程
初始化
+---------------------------------------------------------+
| writable bytes (got more space) |
+---------------------------------------------------------+
| |
0 = readerIndex = writerIndex <= capacity
写入N个字节(N=writerIndex)
+------------------+--------------------------------------+
| readable bytes | writable bytes (got more space) |
+------------------+--------------------------------------+
| | |
readerIndex (0) <= writerIndex (decreased) <= capacity
读取M(M=readerIndex, M<N)个字节
+-------------------+------------------+------------------+
| discardable bytes | readable bytes | writable bytes |
+-------------------+------------------+------------------+
| | | |
0 <= readerIndex <= writerIndex <= capacity
调用discardReadBytes()方法,writerIndex=(N-M)
+------------------+--------------------------------------+
| readable bytes | writable bytes |
+------------------+--------------------------------------+
| | |
readerIndex (0) <= writerIndex (decreased) <= capacity
调用clear()方法
+---------------------------------------------------------+
| writable bytes (got more space) |
+---------------------------------------------------------+
| |
0 = readerIndex = writerIndex <= capacity
1.3 ByteBuf API
1.3.1 顺序读操作(read)
| 名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
readBoolean() |
返回当前readerIndex处的Boolean,并将readerIndex 增加1 |
readByte() |
返回当前readerIndex处的字节,并将readerIndex增加1 |
readUnsignedByte() |
将当前readerIndex处的无符号字节值作为short 返回,并将readerIndex 增加1 |
readMedium() |
返回当前readerIndex处的24位的中等int值,并将readerIndex增加3 |
readUnsignedMedium() |
返回当前readerIndex处的24位的无符号的中等int 值,并将readerIndex增加3 |
readInt() |
返回当前readerIndex的int值,并将readerIndex 增加4 |
readUnsignedInt() |
将当前readerIndex处的无符号的int 值作为long 值返回,并将readerIndex 增加4 |
readLong() |
返回当前readerIndex 处的long值,并将readerIndex 增加8 |
readShort() |
返回当前readerIndex 处的short值,并将readerIndex 增加2 |
readUnsignedShort() |
将当前readerIndex处的无符号short 值作为int 值返回,并将readerIndex 增加2 |
readBytes(ByteBuf byte[] destination,int dstIndex [,intlength]) |
将当前ByteBuf 中从当前readerIndex 处开始的(如果设置了,length 长度的字节)数据传送到一个目标ByteBuf 或者byte[],从目标的dstIndex 开始的位置.本地的readerIndex 将被增加已经传输的字节数 |
1.3.2 顺序写操作(write)
| 名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
writeBoolean(boolean) |
在当前writerIndex处写入一个Boolean,并将writerIndex 增加1 |
writeByte(int) |
在当前writerIndex处写入一个字节值,并将writerIndex 增加1 |
writeMedium(int) |
在当前writerIndex处写入一个中等的int值,并将writerIndex增加3 |
writeInt(int) |
在当前writerIndex处写入一个int值,并将writerIndex 增加4 |
writeLong(long) |
在当前writerIndex处写入一个long值,并将writerIndex 增加8 |
writeShort(int) |
在当前writerIndex处写入一个short值,并将writerIndex 增加2 |
writeBytes(sourceByteBuf byte[][,int srcIndex,int length]) |
从当前writerIndex 开始,传输来自于指定源(ByteBuf 或者byte[])的数据.如果提供了srcIndex 和length,则从srcIndex 开始读取,并且处理长度为length 的字节.当前writerIndex 将会被增加所写入的字节数 |
1.3.3 随机读操作(get)
| 名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
getBoolean(int) |
返回给定索引处的Boolean值 |
getByte(int) |
返回给定索引处的字节 |
getUnsignedByte(int) |
将给定索引处的无符号字节值作为short返回 |
getMedium(int) |
返回给定索引处的24位的中等int值 |
getUnsignedMedium(int) |
返回给定索引处的无符号的24位的中等int值 |
getInt(int) |
返回给定索引处的int值 |
getUnsignedInt(int) |
将给定索引处的无符号int值作为long返回 |
getLong(int) |
返回给定索引处的long值 |
getShort(int) |
返回给定索引处的short值 |
getUnsignedShort(int) |
将给定索引处的无符号short值作为int返回 |
getBytes(int, …) |
将该缓冲区中从给定索引开始的数据传送到指定的目的地 |
1.3.4 随机写操作(set)
| 名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
setBoolean(int, boolean) |
设定给定索引处的Boolean值 |
setByte(int index, int value) |
设定给定索引处的字节值 |
setMedium(int index, int value) |
设定给定索引处的24位的中等int 值 |
setInt(int index, int value) |
设定给定索引处的int值 |
setLong(int index, long value) |
设定给定索引处的long值 |
setShort(int index, int value) |
设定给定索引处的short值 |
注意: set和write不一样,它不支持动态扩展缓冲区,所以使用者必须保证当前的缓冲区字节数大于需要写入的字节长度
1.3.5 其它可用操作
| 名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
isReadable() |
如果至少有一个字节可供读取,则返回true |
isWritable() |
如果至少有一个字节可被写入,则返回true |
readableBytes() |
返回可被读取的字节数 |
writableBytes() |
返回可被写入的字节数 |
capacity() |
返回ByteBuf 可容纳的字节数.在此之后,它会尝试再次扩展直到达到maxCapacity() |
maxCapacity() |
返回ByteBuf 可以容纳的最大字节数 |
hasArray() |
如果ByteBuf 由一个字节数组支撑,则返回true |
array() |
如果 ByteBuf 由一个字节数组支撑则返回该数组;否则,它将抛出一个UnsupportedOperationException 异常 |
1.3.6 复制
| 名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
duplicate |
复制ByteBuf,维护自己的读写索引,但是共享缓冲区内容 |
copy |
复制ByteBuf,不共享内容 |
copy(int index, int length) |
从指定的索引开始复制 |
slice |
返回ByteBuf的可读子缓冲区, 共享内容,维护独立的读写索引 |
slice(int index, int length) |
返回带起始位置的可读子缓冲区,同样共享内容当通过NIO的SocketChannel进行网络读写时,操作的对象是JDK标准的ByteBuffer,因此需要支持ByteBuf到ByteBuffer的互相转换 |
2.源码分析
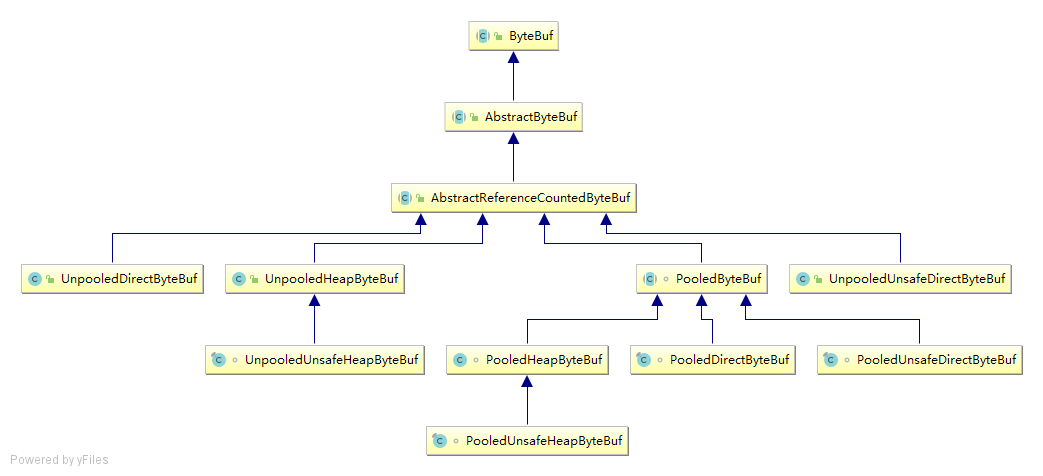
ByteBuf的实现类划分
- 从内存划分角度
HeapByteBuf: 使用堆内存,由JVM进行垃圾回收,但是需要将数据从缓冲区拷贝到内核Channel中DirectByteBuf: 采用堆外内存,回收速度较慢,但是不需要内存复制,速度较快
- 从内存回收角度
- 基于对象池的ByteBuf: 可重用ByteBuf对象,它自己维护了一个内存池,可以循环利用创建的ByteBuf,提升内存的使用效率,降低由于高负载导致的频繁GC.测试表明使用内存池后的Netty在高负载、大并发的冲击下内存和GC更加平稳.
- 和普通ByteBuf
2.1 AbstractByteBuf
主要成员变量
public abstract class AbstractByteBuf extends ByteBuf { static final ResourceLeakDetector<ByteBuf> leakDetector = new ResourceLeakDetector<ByteBuf>(ByteBuf.class); //读指针 int readerIndex; //写指针 int writerIndex; //保存读指针 private int markedReaderIndex; //保存写指针 private int markedWriterIndex; //最大分配容量 private int maxCapacity; protected AbstractByteBuf(int maxCapacity) { if (maxCapacity < 0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("maxCapacity: " + maxCapacity + " (expected: >= 0)"); } this.maxCapacity = maxCapacity; } }读操作
public abstract class AbstractByteBuf extends ByteBuf { @Override public ByteBuf readBytes(ByteBuf dst, int dstIndex, int length) { // 对缓冲区的可用空间进行校验 checkReadableBytes(length); // 从当前的读索引开始, 复制length个字节到目标byte数组中 getBytes(readerIndex, dst, dstIndex, length); // 读取成功,读索引递增 readerIndex += length; return this; } /** * Throws an {@link IndexOutOfBoundsException} if the current * {@linkplain #readableBytes() readable bytes} of this buffer is less * than the specified value. */ protected final void checkReadableBytes(int minimumReadableBytes) { if (minimumReadableBytes < 0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("minimumReadableBytes: " + minimumReadableBytes + " (expected: >= 0)"); } checkReadableBytes0(minimumReadableBytes); } private void checkReadableBytes0(int minimumReadableBytes) { // 是否可访问 ensureAccessible(); // 是否超过写索引,即超过可读段 if (readerIndex > writerIndex - minimumReadableBytes) { throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(String.format( "readerIndex(%d) + length(%d) exceeds writerIndex(%d): %s", readerIndex, minimumReadableBytes, writerIndex, this)); } } /** * 抽象方法, 由子类实现复制操作 * Transfers this buffer's data to the specified destination starting at * the specified absolute {@code index}. * This method does not modify {@code readerIndex} or {@code writerIndex} * of both the source (i.e. {@code this}) and the destination. * * @param dstIndex the first index of the destination * @param length the number of bytes to transfer * * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException * if the specified {@code index} is less than {@code 0}, * if the specified {@code dstIndex} is less than {@code 0}, * if {@code index + length} is greater than * {@code this.capacity}, or * if {@code dstIndex + length} is greater than * {@code dst.capacity} */ public abstract ByteBuf getBytes(int index, ByteBuf dst, int dstIndex, int length); }写操作 ```java public abstract class AbstractByteBuf extends ByteBuf { @Override public ByteBuf writeBytes(byte[] src, int srcIndex, int length) {
// 对写入字节数组的长度进行合法性校验 ensureWritable(length); setBytes(writerIndex, src, srcIndex, length); writerIndex += length; return this;}
@Override public ByteBuf ensureWritable(int minWritableBytes) {
if (minWritableBytes < 0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format( "minWritableBytes: %d (expected: >= 0)", minWritableBytes)); } ensureWritable0(minWritableBytes); return this;}
final void ensureWritable0(int minWritableBytes) { // 检查是否可访问 ensureAccessible(); // 目前容量可写,直接返回 if (minWritableBytes <= writableBytes()) {
return;}
// 超过最大上限,抛出 IndexOutOfBoundsException 异常 if (minWritableBytes > maxCapacity - writerIndex) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(String.format( "writerIndex(%d) + minWritableBytes(%d) exceeds maxCapacity(%d): %s", writerIndex, minWritableBytes, maxCapacity, this));}
// 计算新的容量.默认情况下,2 倍扩容,并且不超过最大容量上限. // Normalize the current capacity to the power of 2. int newCapacity = alloc().calculateNewCapacity(writerIndex + minWritableBytes, maxCapacity);
// 设置新的容量大小 // Adjust to the new capacity. capacity(newCapacity); } }
public abstract class AbstractByteBufAllocator implements ByteBufAllocator { @Override public int calculateNewCapacity(int minNewCapacity, int maxCapacity) { if (minNewCapacity < 0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("minNewCapacity: " + minNewCapacity + " (expected: 0+)"); } if (minNewCapacity > maxCapacity) { throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format( "minNewCapacity: %d (expected: not greater than maxCapacity(%d)", minNewCapacity, maxCapacity)); } final int threshold = CALCULATE_THRESHOLD; // 4 MiB page
// 等于 threshold ,直接返回 threshold .
if (minNewCapacity == threshold) {
return threshold;
}
// 超过 threshold ,增加 threshold ,不超过 maxCapacity 大小.
// If over threshold, do not double but just increase by threshold.
if (minNewCapacity > threshold) {
int newCapacity = minNewCapacity / threshold * threshold;
if (newCapacity > maxCapacity - threshold) { // 不超过 maxCapacity
newCapacity = maxCapacity;
} else {
newCapacity += threshold;
}
return newCapacity;
}
// 未超过 threshold ,从 64 开始两倍计算,不超过 4M 大小.
// Not over threshold. Double up to 4 MiB, starting from 64.
int newCapacity = 64;
while (newCapacity < minNewCapacity) {
newCapacity <<= 1;
}
return Math.min(newCapacity, maxCapacity);
}
}
4. 索引操作
```java
public abstract class AbstractByteBuf extends ByteBuf {
@Override
public ByteBuf readerIndex(int readerIndex) {
if (readerIndex < 0 || readerIndex > writerIndex) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(String.format(
"readerIndex: %d (expected: 0 <= readerIndex <= writerIndex(%d))", readerIndex, writerIndex));
}
this.readerIndex = readerIndex;
return this;
}
@Override
public ByteBuf markReaderIndex() {
markedReaderIndex = readerIndex;
return this;
}
@Override
public ByteBuf resetReaderIndex() {
readerIndex(markedReaderIndex);
return this;
}
}
重用缓冲区
public abstract class AbstractByteBuf extends ByteBuf { @Override public ByteBuf discardReadBytes() { // 校验可访问 ensureAccessible(); // 无废弃段,直接返回 if (readerIndex == 0) { return this; } // 未读取完 if (readerIndex != writerIndex) { // 将可读段复制到 ByteBuf 头 setBytes(0, this, readerIndex, writerIndex - readerIndex); // 写索引减小 writerIndex -= readerIndex; // 调整标记位 adjustMarkers(readerIndex); // 读索引重置为 0 readerIndex = 0; // 全部读取完 } else { // 调整标记位 adjustMarkers(readerIndex); // 读写索引都重置为 0 writerIndex = readerIndex = 0; } return this; } protected final void adjustMarkers(int decrement) { int markedReaderIndex = this.markedReaderIndex; // 读标记位小于减少值(decrement) if (markedReaderIndex <= decrement) { // 重置读标记位为 0 this.markedReaderIndex = 0; // 写标记位小于减少值(decrement) int markedWriterIndex = this.markedWriterIndex; if (markedWriterIndex <= decrement) { // 重置写标记位为 0 this.markedWriterIndex = 0; // 减小写标记位 } else { this.markedWriterIndex = markedWriterIndex - decrement; } // 减小读写标记位 } else { this.markedReaderIndex = markedReaderIndex - decrement; this.markedWriterIndex -= decrement; } } }
6.跳过字节
public abstract class AbstractByteBuf extends ByteBuf {
@Override
public ByteBuf skipBytes(int length) {
checkReadableBytes(length);
readerIndex += length;
return this;
}
}
2.2 AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf
该类主要是对引用进行计数,类似于JVM内存回收的对象引用计数器,用户跟踪对象的分配和销毁,做自动内存回收.
成员变量
public abstract class AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf extends AbstractByteBuf { /** * {@link #refCnt} 的更新器 */ private static final AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf> refCntUpdater = AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf.class, "refCnt"); /** * 引用计数 */ private volatile int refCnt; protected AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf(int maxCapacity) { // 设置最大容量 super(maxCapacity); // 初始 refCnt 为 1 refCntUpdater.set(this, 1); } }对象引用计数器
public abstract class AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf extends AbstractByteBuf { @Override public ByteBuf retain() { return retain0(1); } private ByteBuf retain0(final int increment) { // 增加 int oldRef = refCntUpdater.getAndAdd(this, increment); // 原有 refCnt 就是 <= 0 ;或者,increment 为负数 if (oldRef <= 0 || oldRef + increment < oldRef) { // Ensure we don't resurrect (which means the refCnt was 0) and also that we encountered an overflow. // 加回去,负负得正. refCntUpdater.getAndAdd(this, -increment); // 抛出 IllegalReferenceCountException 异常 throw new IllegalReferenceCountException(oldRef, increment); } return this; } @Override public boolean release() { return release0(1); } @SuppressWarnings("Duplicates") private boolean release0(int decrement) { // 减少 int oldRef = refCntUpdater.getAndAdd(this, -decrement); // 原有 oldRef 等于减少的值 if (oldRef == decrement) { // 释放 deallocate(); return true; // 减少的值得大于 原有 oldRef ,说明"越界";或者,increment 为负数 } else if (oldRef < decrement || oldRef - decrement > oldRef) { // Ensure we don't over-release, and avoid underflow. // 加回去,负负得正. refCntUpdater.getAndAdd(this, decrement); // 抛出 IllegalReferenceCountException 异常 throw new IllegalReferenceCountException(oldRef, -decrement); } return false; } }
2.3 UnpooledHeapByteBuf
UnpooledHeapByteBuf是基于堆内存进行内存分配的字节缓冲区,它并没有基于对象池技术实现,这就以为着每次I/O的读写都会创建一个新的 UnpooledHeapByteBuf ,频繁进行大块内存的分配和回收对性能会造成一定的影响,但是相比于堆外内存的申请和释放,它的成本还是会低一些.
在满足于性能的情况下, 推荐使用UnpooledHeapByteBuf.
成员变量
public class UnpooledHeapByteBuf extends AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf { /** * ByteBuf 分配器对象 */ private final ByteBufAllocator alloc; /** * 字节数组 */ byte[] array; /** * 临时 ByteBuff 对象 */ private ByteBuffer tmpNioBuf; /** * Creates a new heap buffer with an existing byte array. * * @param initialArray the initial underlying byte array * @param maxCapacity the max capacity of the underlying byte array */ protected UnpooledHeapByteBuf(ByteBufAllocator alloc, byte[] initialArray, int maxCapacity) { // 设置最大容量 super(maxCapacity); checkNotNull(alloc, "alloc"); checkNotNull(initialArray, "initialArray"); if (initialArray.length > maxCapacity) { throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format( "initialCapacity(%d) > maxCapacity(%d)", initialArray.length, maxCapacity)); } this.alloc = alloc; // 设置字节数组 setArray(initialArray); // 设置读写索引 setIndex(0, initialArray.length); } }动态扩展缓冲区
public class UnpooledHeapByteBuf extends AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf { @Override public ByteBuf capacity(int newCapacity) { // // 校验新的容量,不能超过最大容量 checkNewCapacity(newCapacity); int oldCapacity = array.length; byte[] oldArray = array; // 扩容 if (newCapacity > oldCapacity) { // 创建新数组 byte[] newArray = allocateArray(newCapacity); // 复制【全部】数据到新数组 System.arraycopy(oldArray, 0, newArray, 0, oldArray.length); // 设置数组 setArray(newArray); // 释放老数组 freeArray(oldArray); // 缩容 } else if (newCapacity < oldCapacity) { // 创建新数组 byte[] newArray = allocateArray(newCapacity); int readerIndex = readerIndex(); if (readerIndex < newCapacity) { // 如果写索引超过新容量,需要重置下,设置为最大容量.否则就越界了. int writerIndex = writerIndex(); if (writerIndex > newCapacity) { writerIndex(writerIndex = newCapacity); } // 只复制【读取段】数据到新数组 System.arraycopy(oldArray, readerIndex, newArray, readerIndex, writerIndex - readerIndex); } else { // 因为读索引超过新容量,所以写索引超过新容量 // 如果读写索引都超过新容量,需要重置下,都设置为最大容量.否则就越界了. setIndex(newCapacity, newCapacity); // 这里要注意下,老的数据,相当于不进行复制,因为已经读取完了. } // 设置数组 setArray(newArray); // 释放老数组 freeArray(oldArray); } return this; } }字节数组的复制
public class UnpooledHeapByteBuf extends AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf { @Override public ByteBuf setBytes(int index, ByteBuf src, int srcIndex, int length) { checkSrcIndex(index, length, srcIndex, src.capacity()); if (src.hasMemoryAddress()) { PlatformDependent.copyMemory(src.memoryAddress() + srcIndex, array, index, length); } else if (src.hasArray()) { setBytes(index, src.array(), src.arrayOffset() + srcIndex, length); } else { src.getBytes(srcIndex, array, index, length); } return this; } @Override public ByteBuf setBytes(int index, byte[] src, int srcIndex, int length) { checkSrcIndex(index, length, srcIndex, src.length); System.arraycopy(src, srcIndex, array, index, length); return this; } }转换成JDK ByteBuffer ```java // JDB ByteBuffer public abstract class ByteBuffer extends Buffer implements Comparable
{ public static ByteBuffer wrap(byte[] array, int offset, int length){ try { return new HeapByteBuffer(array, offset, length); } catch (IllegalArgumentException x) { throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(); }} }
// UnpooledHeapByteBuf warp public class UnpooledHeapByteBuf extends AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf { @Override public ByteBuffer nioBuffer(int index, int length) { ensureAccessible(); return ByteBuffer.wrap(array, index, length).slice(); } }
5. 其它
```java
public class UnpooledHeapByteBuf extends AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf {
@Override
public boolean isDirect() {
// 是否基于堆内存实现的ByteBuf
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean hasArray() {
// 是否基于字节数组实现
return true;
}
}
2.4 UnpooledDirectByteBuf
内存缓冲区由java.nio.DirectByteBuffer实现
成员变量
public class UnpooledDirectByteBuf extends AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf { /** * ByteBuf 分配器对象 */ private final ByteBufAllocator alloc; /** * 数据 ByteBuffer 对象 */ private ByteBuffer buffer; /** * 临时 ByteBuffer 对象 */ private ByteBuffer tmpNioBuf; /** * 容量 */ private int capacity; /** * 是否需要释放 * * 如果 {@link #buffer} 从外部传入,则需要进行释放,即 {@link #UnpooledDirectByteBuf(ByteBufAllocator, ByteBuffer, int)} 构造方法. */ private boolean doNotFree; /** * Creates a new direct buffer by wrapping the specified initial buffer. * * @param maxCapacity the maximum capacity of the underlying direct buffer */ protected UnpooledDirectByteBuf(ByteBufAllocator alloc, ByteBuffer initialBuffer, int maxCapacity) { // 设置最大容量 super(maxCapacity); if (alloc == null) { throw new NullPointerException("alloc"); } if (initialBuffer == null) { throw new NullPointerException("initialBuffer"); } if (!initialBuffer.isDirect()) { // 必须是 Direct throw new IllegalArgumentException("initialBuffer is not a direct buffer."); } if (initialBuffer.isReadOnly()) { // 必须可写 throw new IllegalArgumentException("initialBuffer is a read-only buffer."); } // 获得剩余可读字节数,作为初始容量大小 int initialCapacity = initialBuffer.remaining(); if (initialCapacity > maxCapacity) { throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format( "initialCapacity(%d) > maxCapacity(%d)", initialCapacity, maxCapacity)); } this.alloc = alloc; // 标记为 true .因为 initialBuffer 是从外部传递进来,释放的工作,不交给当前 UnpooledDirectByteBuf 对象. doNotFree = true; // slice 切片 // 设置数据 ByteBuffer 对象 setByteBuffer(initialBuffer.slice().order(ByteOrder.BIG_ENDIAN)); // 设置写索引 writerIndex(initialCapacity); } }动态扩展缓冲区
public class UnpooledDirectByteBuf extends AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf { @Override public ByteBuf capacity(int newCapacity) { // 校验新的容量,不能超过最大容量 checkNewCapacity(newCapacity); int readerIndex = readerIndex(); int writerIndex = writerIndex(); int oldCapacity = capacity; // 扩容 if (newCapacity > oldCapacity) { ByteBuffer oldBuffer = buffer; // 创建新的 Direct ByteBuffer 对象 ByteBuffer newBuffer = allocateDirect(newCapacity); // 复制数据到新的 buffer 对象 oldBuffer.position(0).limit(oldBuffer.capacity()); newBuffer.position(0).limit(oldBuffer.capacity()); newBuffer.put(oldBuffer); newBuffer.clear(); // 因为读取和写入,使用 readerIndex 和 writerIndex ,所以没关系. // 设置新的 buffer 对象,并根据条件释放老的 buffer 对象 setByteBuffer(newBuffer); // 缩容 } else if (newCapacity < oldCapacity) { ByteBuffer oldBuffer = buffer; // 创建新的 Direct ByteBuffer 对象 ByteBuffer newBuffer = allocateDirect(newCapacity); if (readerIndex < newCapacity) { // 如果写索引超过新容量,需要重置下,设置为最大容量.否则就越界了. if (writerIndex > newCapacity) { writerIndex(writerIndex = newCapacity); } // 复制数据到新的 buffer 对象 oldBuffer.position(readerIndex).limit(writerIndex); newBuffer.position(readerIndex).limit(writerIndex); newBuffer.put(oldBuffer); newBuffer.clear(); // 因为读取和写入,使用 readerIndex 和 writerIndex ,所以没关系. } else { // 因为读索引超过新容量,所以写索引超过新容量 // 如果读写索引都超过新容量,需要重置下,都设置为最大容量.否则就越界了. setIndex(newCapacity, newCapacity); // 这里要注意下,老的数据,相当于不进行复制,因为已经读取完了. } // 设置新的 buffer 对象,并根据条件释放老的 buffer 对象 setByteBuffer(newBuffer); } return this; } }
3.辅助类
3.1 ByteBufHolder
是ByteBuf的容器,它包含了一个ByteBuf,另外还提供其他实用的方法,使用者继承ByteBufHolder接口后便可以按需封装自己的实现
public interface ByteBufHolder extends ReferenceCounted {
/**
* 返回由这个ByteBufHolder所持有的ByteBuf
* Return the data which is held by this {@link ByteBufHolder}.
*/
ByteBuf content();
/**
* 返回这个ByteBufHolder得一个深拷贝,包括一个其所包含的ByteBuf的非共享拷贝
* Creates a deep copy of this {@link ByteBufHolder}.
*/
ByteBufHolder copy();
/**
* 返回这个ByteBufHolder的以个浅拷贝,包括一个其所包含的ByteBuf的共享拷贝
* Duplicates this {@link ByteBufHolder}. Be aware that this will not automatically call {@link #retain()}.
*/
ByteBufHolder duplicate();
/**
* Duplicates this {@link ByteBufHolder}. This method returns a retained duplicate unlike {@link #duplicate()}.
*
* @see ByteBuf#retainedDuplicate()
*/
ByteBufHolder retainedDuplicate();
/**
* Returns a new {@link ByteBufHolder} which contains the specified {@code content}.
*/
ByteBufHolder replace(ByteBuf content);
@Override
ByteBufHolder retain();
@Override
ByteBufHolder retain(int increment);
@Override
ByteBufHolder touch();
@Override
ByteBufHolder touch(Object hint);
}
3.2 ByteBufAllocator
字节缓冲分配器,有两种
- 基于内存池的字节缓冲区分配器
- 普通的字节缓冲区分配器
| 名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
buffer()buffer(int initialCapacity)buffer(int initialCapacity, int maxCapacity) |
返回一个基于堆或者直接内存存储的ByteBuf |
heapBuffer()heapBuffer(int initialCapacity)heapBuffer(int initialCapacity, int maxCapacity) |
返回一个基于堆内存存储的ByteBuf |
directBuffer()directBuffer(int initialCapacity)directBuffer(int initialCapacity, int maxCapacity) |
返回一个基于直接内存存储的ByteBuf |
compositeBuffer()compositeBuffer(int maxNumComponents)heapCompositeBuffer()heapCompositeBuffer(int maxNumComponents)directCompositeBuffer()directCompositeBuffer(int maxNumComponents) |
返回一个可以通过添加最大到指定数目的基于堆的或者直接内存存储的缓冲区来扩展的CompositeByteBuf |
ioBuffer() |
返回一个用于套接字的I/O操作的ByteBuf |
3.3 CompositeByteBuf
- 聚合多个ByteBuf时不需要copy,形成一个统一的视图,对外提供统一的readindex和writerindex
- 有个ComponentList,继承ArrayList,聚合的bytebuf都放在ComponentList里面,最小容量为16
3.3.1 内部类
/**
* A virtual buffer which shows multiple buffers as a single merged buffer. It is recommended to use
* {@link ByteBufAllocator#compositeBuffer()} or {@link Unpooled#wrappedBuffer(ByteBuf...)} instead of calling the
* constructor explicitly. 复合直接为一个虚拟的buf,将多个buf展示为一个合并的buf.强烈建议使用ByteBufAllocator#compositeBuffer() Unpooled#wrappedBuffer(ByteBuf...)构造复合buf.
*/
public class CompositeByteBuf extends AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf implements Iterable<ByteBuf> {
private static final ByteBuffer EMPTY_NIO_BUFFER = Unpooled.EMPTY_BUFFER.nioBuffer();
private static final Iterator<ByteBuf> EMPTY_ITERATOR = Collections.<ByteBuf>emptyList().iterator();
// 字节buf分配器
private final ByteBufAllocator alloc;
// 是否为direct buf
private final boolean direct;
// 字节buf集合
private final ComponentList components;
// buf即最大容量
private final int maxNumComponents;
private static final class Component {
// 内部字节buf
final ByteBuf buf;
// buf字节长度
final int length;
// 在复合buf中的开始位置
int offset;
// 在复合buf中的结束位置
int endOffset;
Component(ByteBuf buf) {
this.buf = buf;
length = buf.readableBytes();
}
void freeIfNecessary() {
buf.release(); // We should not get a NPE here. If so, it must be a bug.
}
}
private static final class ComponentList extends ArrayList<Component> {
ComponentList(int initialCapacity) {
super(initialCapacity);
}
// Expose this methods so we not need to create a new subList just to remove a range of elements.
@Override
public void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
super.removeRange(fromIndex, toIndex);
}
}
}
3.3.2 添加ByteBuf
public class CompositeByteBuf extends AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf implements Iterable<ByteBuf> {
/**
* Add the given {@link ByteBuf} and increase the {@code writerIndex} if {@code increaseWriterIndex} is
* {@code true}.
*
* {@link ByteBuf#release()} ownership of {@code buffer} is transfered to this {@link CompositeByteBuf}.
* @param buffer the {@link ByteBuf} to add. {@link ByteBuf#release()} ownership is transfered to this
* {@link CompositeByteBuf}.
*/
public CompositeByteBuf addComponent(boolean increaseWriterIndex, ByteBuf buffer) {
checkNotNull(buffer, "buffer");
addComponent0(increaseWriterIndex, components.size(), buffer);
// 判断是否需要进行扩容
consolidateIfNeeded();
return this;
}
/**
* Precondition is that {@code buffer != null}.
*/
private int addComponent0(boolean increaseWriterIndex, int cIndex, ByteBuf buffer) {
assert buffer != null;
boolean wasAdded = false;
try {
// 检查cIndex是否超过ComponentList的容量
checkComponentIndex(cIndex);
int readableBytes = buffer.readableBytes();
// No need to consolidate - just add a component to the list.
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
// 封装为Component,采用大端序
Component c = new Component(buffer.order(ByteOrder.BIG_ENDIAN).slice());
// 比如第一次聚合的时候,cIndex=0,components.size() = 0
if (cIndex == components.size()) {
wasAdded = components.add(c);
if (cIndex == 0) {
// 如果是第一个buffer,则该Component的endOffset为buffer的大小
c.endOffset = readableBytes;
} else {
//如果不是第一个buffer,则该buffer的offset为上一个的endOffset
Component prev = components.get(cIndex - 1);
c.offset = prev.endOffset;
c.endOffset = c.offset + readableBytes;
}
} else {
components.add(cIndex, c);
wasAdded = true;
if (readableBytes != 0) {
updateComponentOffsets(cIndex);
}
}
if (increaseWriterIndex) {
writerIndex(writerIndex() + buffer.readableBytes());
}
return cIndex;
} finally {
if (!wasAdded) {
buffer.release();
}
}
}
}
3.3.3 CompositeByteBuf扩容
public class CompositeByteBuf extends AbstractReferenceCountedByteBuf implements Iterable<ByteBuf> {
/**
* This should only be called as last operation from a method as this may adjust the underlying
* array of components and so affect the index etc.
*/
private void consolidateIfNeeded() {
// Consolidate if the number of components will exceed the allowed maximum by the current
// operation.
final int numComponents = components.size();
if (numComponents > maxNumComponents) {
final int capacity = components.get(numComponents - 1).endOffset;
//创建一个大的bytebuf,容量会所有bytebuf的总和
ByteBuf consolidated = allocBuffer(capacity);
// We're not using foreach to avoid creating an iterator.
for (int i = 0; i < numComponents; i ++) {
Component c = components.get(i);
ByteBuf b = c.buf;
//copy c的数据到consolidated
consolidated.writeBytes(b);
// 释放c的资源
c.freeIfNecessary();
}
Component c = new Component(consolidated);
c.endOffset = c.length;
components.clear();
components.add(c);
}
}
}
3.4 ByteBufUtil
非常有用的工具类,用于操作ByteBuf对象,比如提供了对字符串编码和解码的功能
| 名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
encodeString() |
对字符串进行编码,生存ByteBuf对象 |
decodeString() |
对字符串进行解码,生存ByteBuf对象 |
hexDump() |
能够将参数ByteBuf的内容转换为十六进制的字符串 |